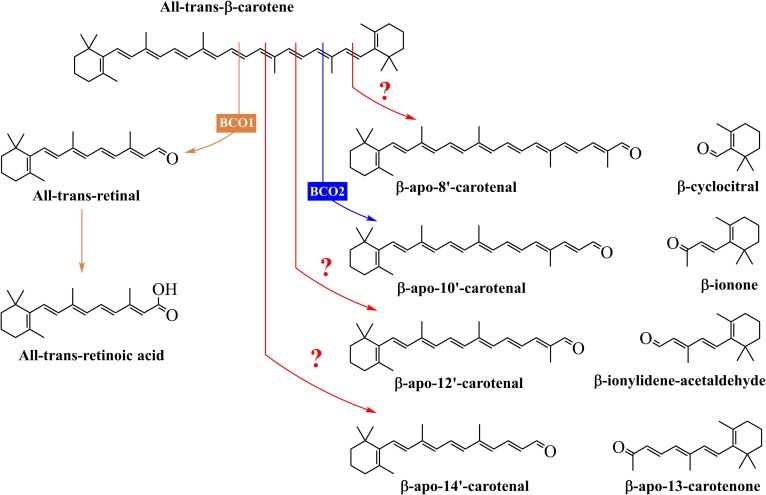
Fig. 1.
Structures of the products of the central and eccentric cleavage of β-carotene. All-trans-β-carotene can be cleaved by BCO1 to yield two molecules of retinal, which can be converted to retinol or RA. On the other hand, the main product of the eccentric cleavage pathway of β-carotene is β-apo-10′-carotenal, and this reaction is catalyzed by BCO2. Also, β-carotene can undergo chemical and enzymatic oxidations in vivo and in foods to yield other long-chain and short-chain β-apocarotenoids. The exact mechanisms and enzymes responsible for these products are unknown.