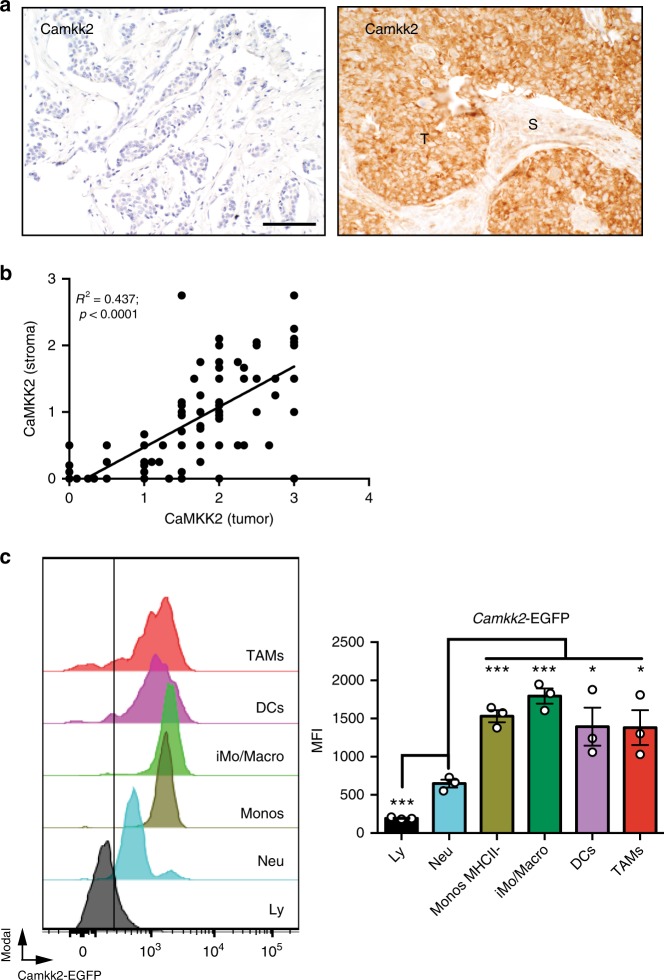
Fig. 1.
CaMKK2 is expressed in mammary tumor-associated stromal cells. a Expression of CaMKK2 in human breast cancer. Representative images (×400 magnification) of malignant mammary tissue samples stained with an anti-CaMKK2 antibody. T and S refer to tumor and stromal cells, respectively. Scale bar = 100 μm. b CaMKK2 staining intensity is correlated between cancer and stromal cells of the same human breast tumors. c The Camkk2 promoter is active in myeloid cells associated with mammary tumors. E0771 cells (4 × 105 cells/mouse) were inoculated into the mammary fat pad of (Tg)-Camkk2-EGFP reporter mice. Subsequently, tumors were removed and digested and single-cell suspensions were stained for markers of myeloid cells. The gating strategy used to identify myeloid subsets and lymphoid cells is shown in Supplementary Fig. 1B. (Left) FACS profiles report the expression of EGFP reporter in tumor-associated immune cells. The vertical line refers to negative control (EGFP-negative splenocytes). (Right) Mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of EGFP expression in immune cell subsets. Bar graph reports the mean ± SEM (standard error of the mean; N = 3 independent tumors in each group). *p < 0.05, ****p < 0.005, respectively. A t test was used to calculate p-values. Similar results have been observed in three independent experiments