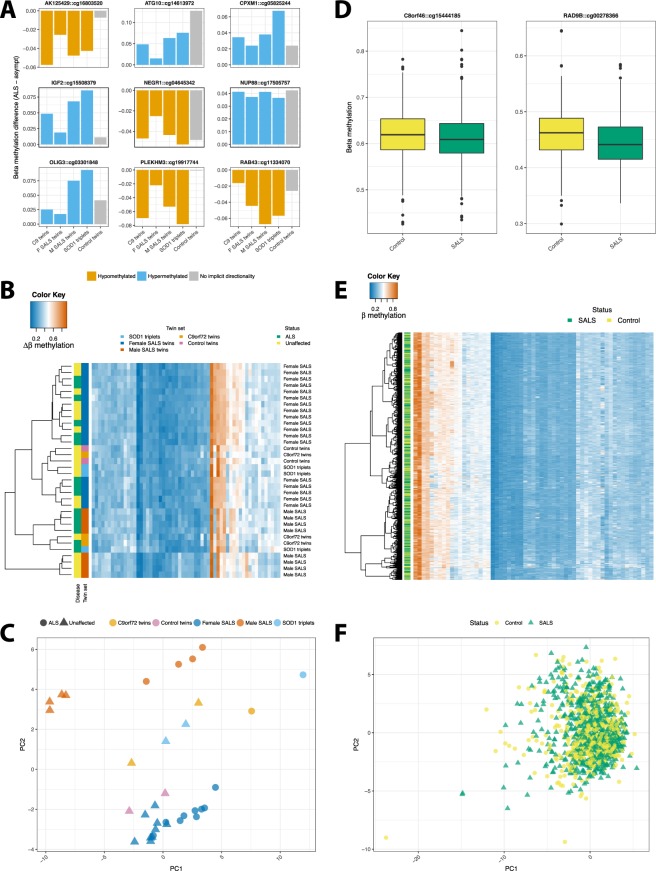
Figure 4.
Top identified DMPs do not cluster by disease in MZ and case-control cohorts. (A) Of 59 DMPs found across all discordant twin sets, these 9 were top ranked for the combination of statistical significantly differences between affected and unaffected co-twins/-triplets and the magnitude of differences across twin/triplet sets. Per twin/triplet set differences are shown, with the ALS-affected sibling as the reference for direction of methylation. Gene annotation and CpG name are indicated as gene::cpg. Bar colour indicates hypomethylation of the ALS-affected twin (orange) or hypermethylation of the affected twin/triplet (blue) relative to their unaffected co-twin/-triplets. Grey bars represent the magnitude of difference in methylation in the control twin set and thus have no implicit directionality. They are shown with the same directionality as the discordant twins to facilitate comparison of the magnitude of the difference in methylation. (B) The 59 DMPs identified across discordant twin/triplet sets were used to cluster the samples in the MZ cohort (n = 34). Overall, methylation was similar across samples for most DMPs, and samples did not cluster by disease, nor perfectly by twin/triplet set. (C) Principal Components Analysis (PCA) across discordant twin/triplet sets and the control twin set using the same 59 DMPs also showed that samples did not cluster by disease, but approximately by individual for those where longitudinal samples were available. (D) Of the 59 DMPs identified across discordant twin/triplet sets, two were significantly different between cases (SALS) and controls in a large extended cohort (n SALS = 646, n controls = 533). Both cg15444185, annotated to C8orf46, and cg00278366, annotated to RAD9B, were hypomethylated in SALS samples (cg15444185, β = −0.06, adjusted p = 0.049; cg00278366, β = −0.0771, adjusted p = 2.5E-5) when controlling for age and sex. (E) The top 59 DMPs identified across all discordant twin set do not cluster by disease status in a sporadic case control cohort. (F) PCA also demonstrates that these top 59 twin DMPs do not cluster by disease status in a sporadic case control cohort.