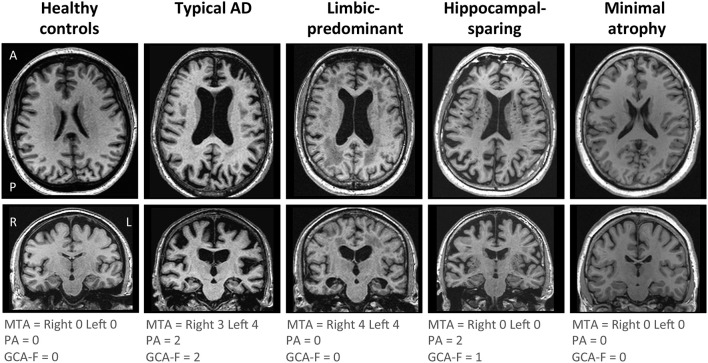
Figure 1.
Visual examples of the brain atrophy patterns in the different AD subtypes. Atrophy patterns were determined based on the combination of MTA, PA, and GCA-F visual rating scales. In the three visual rating scales, a score of zero denotes no atrophy, whereas scores from one to three (PA and GCA-F) or four (MTA) indicate an increasing degree of atrophy. Typical AD was defined as abnormal MTA together with abnormal PA and/or abnormal GCA-F. Limbic-predominant was defined as abnormal MTA alone with normal PA and GCA-F. Hippocampal-sparing included abnormal PA and/or abnormal GCA-F, but normal MTA. Minimal atrophy AD was defined as normal scores in MTA, PA, and GCA-F. The figure shows examples for each AD subtype and the healthy controls. A, anterior part of the brain; AD, Alzheimer's disease; GCA-F, global cortical atrophy scale–frontal subscale; L, left; MTA, medial temporal atrophy scale; P, posterior part of the brain; PA, posterior atrophy scale; R, right.