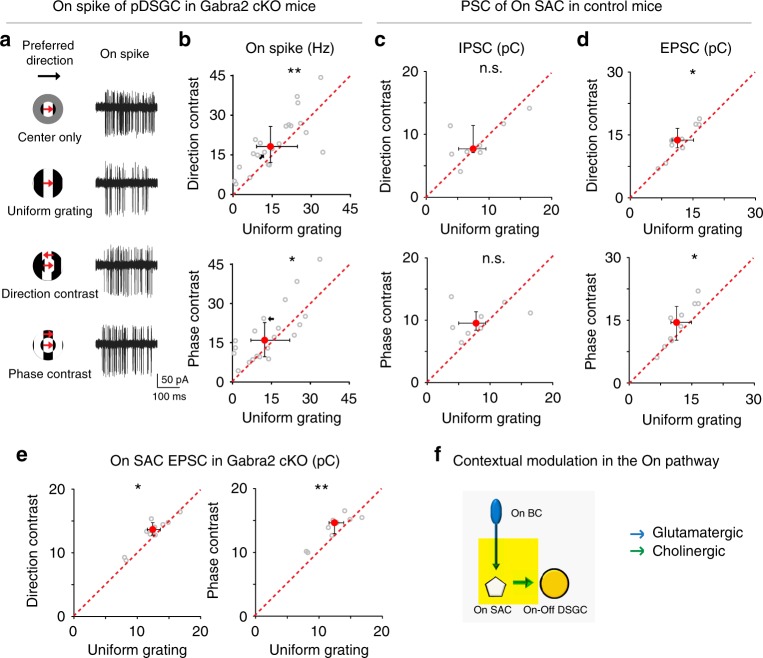
Fig. 5.
The contextual sensitivity of pDSGCs and On SACs is mediated by the excitatory inputs but not inhibitory inputs onto On SACs. a On spike traces of an example pDSGC from a Gabra2 cKO mouse under different stimulus conditions. See also Supplementary Fig. 6a for example EPSC traces from a pDSGC in Gabra2 cKO mouse. b Scatter plots compare pDSGC On spike firing rate during uniform grating versus compound gratings in Gabra2 cKO mice. Direction-contrast vs uniform grating: n = 22 cells from 12 mice, **p = 0.0094; Phase-contrast vs uniform grating: n = 20 cells from 12 mice, *p = 0.048. Wilcoxon signed-rank tests were used in this and subsequent scatter plots. See also Supplementary Fig. 6b for comparison of On EPSC charge transfer of pDSGCs in Gabra2 cKO mice. c Scatter plots of On SAC inhibitory charge transfer in control mice, n = 8 cells from 4 mice. Direction-contrast vs uniform grating: p = 0.95; Phase-contrast vs uniform grating: p = 0.15. d Scatter plots of On SAC excitatory charge transfer in control mice, n = 10 cells from 4 mice. Direction-contrast vs uniform grating: *p = 0.020; Phase-contrast vs uniform grating: *p = 0.027. e Scatter plots of On SAC excitatory charge transfer in Gabra2 KO mice, n = 10 cells from 2 mice. Direction-contrast vs uniform grating: *p = 0.037; Phase-contrast vs uniform grating: **p = 0.0098. f Schematic diagram shows the acetylcholine release of On SAC is contextually modulated by On BC – On SAC excitatory inputs