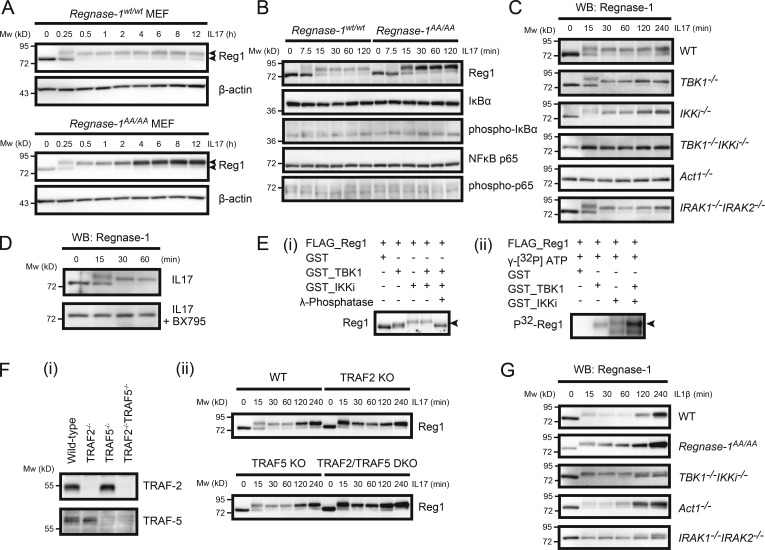
Figure 2.
Regnase-1 phosphorylation by TBK1 and IKKi upon IL-17 stimulation. (A–D) Immunoblotting analysis of Regnase-1 (Reg1) and β-actin (A) and Regnase-1, IκB, phospho-IκB, NF-κB p65, and phospho-NF-κB p65 (B) in WT and Regnase-1AA/AA MEFs; (C) Regnase-1 in WT, TBK1-deficient, IKKi-deficient, TBK1 and IKKi double-deficient, Act1-deficient, and IRAK-1 and IRAK-2 double-deficient MEFs; (D) Regnase-1 in WT MEFs treated without (top) or with (bottom) BX795 (50 µM). MEFs were stimulated with IL-17A (50 ng/ml) for the indicated time. Two arrows in A indicate phosphorylated (top) and unphosphorylated (bottom) forms of Regnase-1. (E) In vitro phosphorylation of Regnase-1 by TBK1 and IKKi. Purified Regnase-1, obtained from Regnase-1–deficient MEFs expressing FLAG-tagged Regnase-1 AA mutant, was incubated with recombinant TBK1 and/or IKKi in the presence or absence of γ-phosphatase for 3 h. Regnase-1 phosphorylation was analyzed by immunoblotting (i) and [32P]-autoradiography (ii). The arrows indicate phosphorylated Regnase-1. (F) IL-17–induced Regnase-1 phosphorylation in WT, TRAF2-deficient, TRAF5-deficient, and TRAF2/TRAF5 double-deficient MEF cell lines. Immunoblotting analysis of TRAF-2 and TRAF-5 (i) and Regnase-1 (ii) in these MEF cell lines. MEFs were stimulated with IL-17A (50 ng/ml) for the indicated times. (G) Immunoblotting analysis of Regnase-1 expression in WT, Regnase-1AA/AA, TBK1/IKKi double-deficient, Act1-deficient, and IRAK1/IRAK2 double-deficient MEFs. Cells were stimulated with IL-1β for 0–240 min. Mw, molecular weight. WB, Western blotting.