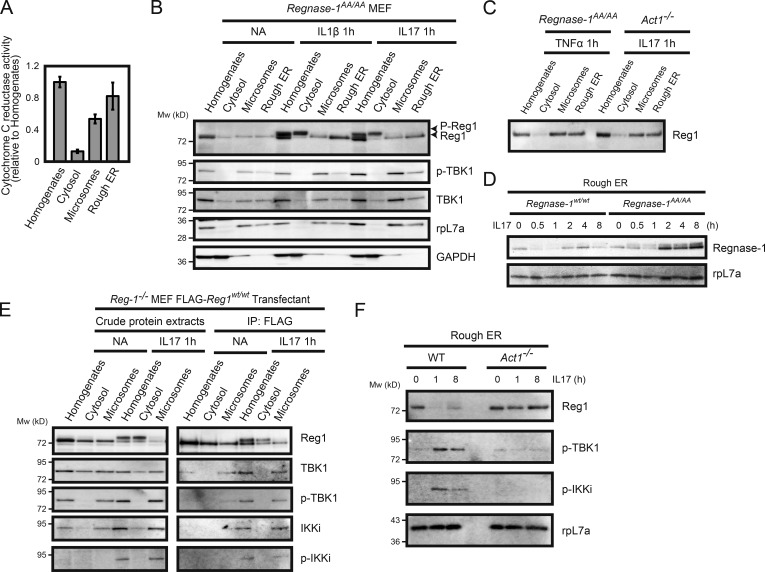
Figure 5.
Regnase-1 phosphorylation and its translocation from the ER membrane. (A) Isolation of ER membrane–containing subcellular organelles from cell homogenates. The purity of each fraction was evaluated through the measurement of activity of cytochrome c reduction by NADP reduced (NADPH)–cytochrome c reductase (n = 4). (B and C) Immunoblotting analysis of subcellular organelle fractions. Regnase-1 (Reg1), ribosomal protein L7a (rpL7a; ER marker), and GAPDH (cytoplasmic marker) in the cell homogenates, soluble cytoplasmic fraction, microsomes, and rough ER membranes. Fractions were prepared from Regnase-1AA/AA MEFs stimulated with IL-1β (10 ng/ml) and IL-17A (50 ng/ml) for 1 h (B) and from Regnase-1AA/AA and Act1-deficient MEFs stimulated with TNF-α (20 ng/ml) and IL-17A (50 ng/ml) for 1 h (C). Arrows indicate phosphorylated (top) and unphosphorylated (bottom) forms of Regnase-1. (D) Immunoblotting analysis of Regnase-1 and rpL7a in rough ER membranes prepared from WT and Regnase-1AA/AA MEFs stimulated with IL-17A (50 ng/ml) for 0–8 h. (E) FLAG-tagged Regnase-1 was immunoprecipitated from cell organelle fractions of Regnase1-deficient MEFs expressing FLAG-tagged Regnase-1 AA mutant stimulated with or without IL-17A (50 ng/ml) for 1 h. Immunoprecipitates were subjected to immunoblotting analysis of Regnase-1, TBK1, phospho-TBK1, IKKi, and phospho-IKKi. (F) Immunoblotting analysis of Regnase-1, phospho-TBK1, phospho-IKKi, and rpL7a in the ER membrane fractions isolated from WT and Act1-deficient MEFs. Cells were stimulated with IL-17A (50 ng/ml) for 0, 1, and 8 h.