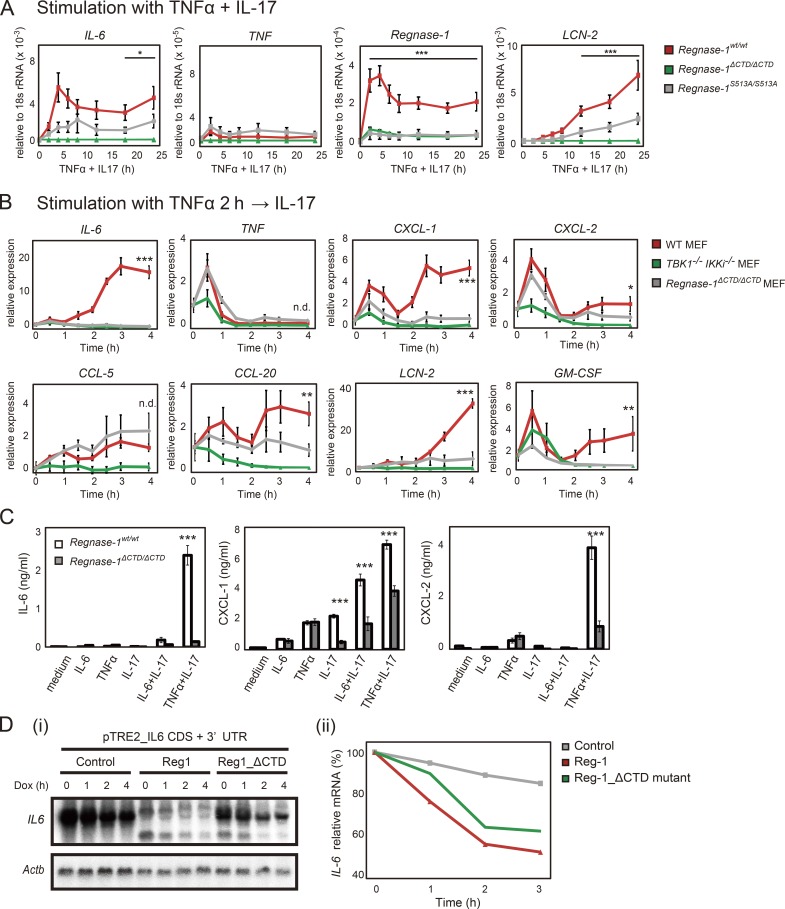
Figure 9.
Regnase-1 ΔCTD and S513A mutations reduce mRNA stability of Regnase-1-targeted genes during IL-17 stimulation. (A) Quantitative PCR (qPCR) of indicated mRNAs in WT, Regnase-1ΔCTD/ΔCTD, and Regnase-1S513A/S513A MEFs (n = 4). Cells were stimulated as indicated for 0–24 h. *, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.005. (B) qPCR analysis of IL-6, TNF, CXCL-1, CXCL-2, CCL-5, CCL20, LCN-2, and GM-CSF expression in WT, Regnase-1 ΔCTD mutant, and TBK1/IKKi double-deficient MEFs. Cells were stimulated with TNF-α (20 ng/ml) for 2 h, followed by IL-17A (50 ng/ml) for 0–4 h. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.005. n.d., no difference. (C) Production of IL-6, CXCL-1, and CXCL-2 by WT and Regnase-1ΔCTD/ΔCTD MEFs in response to exposure to IL-6 (20 ng/ml), TNF-α (20 ng/ml), IL-17A (50 ng/ml), IL-6+IL-17A, or TNF-α+IL-17A for 24 h. Protein levels in cell supernatants were assessed by ELISA (n = 3). ***, P < 0.005. (D) i: Autoradiography of IL-6 (top) and Actb (bottom) mRNA levels in Tet-off HEK293 cells cotransfected with a pTRE-tight-IL6-CDS+3′-UTR vector, together with expression plasmids of control (empty vector), Regnase-1, or ΔCTD mutant. Total mRNA was prepared from cells after treatment with doxycycline (Dox) for 0–4 h, then subjected to Northern blotting. ii: Relative IL-6 mRNA levels in Tet-off HEK293 cells during doxycycline treatment. GM-CSF, granulocyte macrophage CSF; Mw, molecular weight.