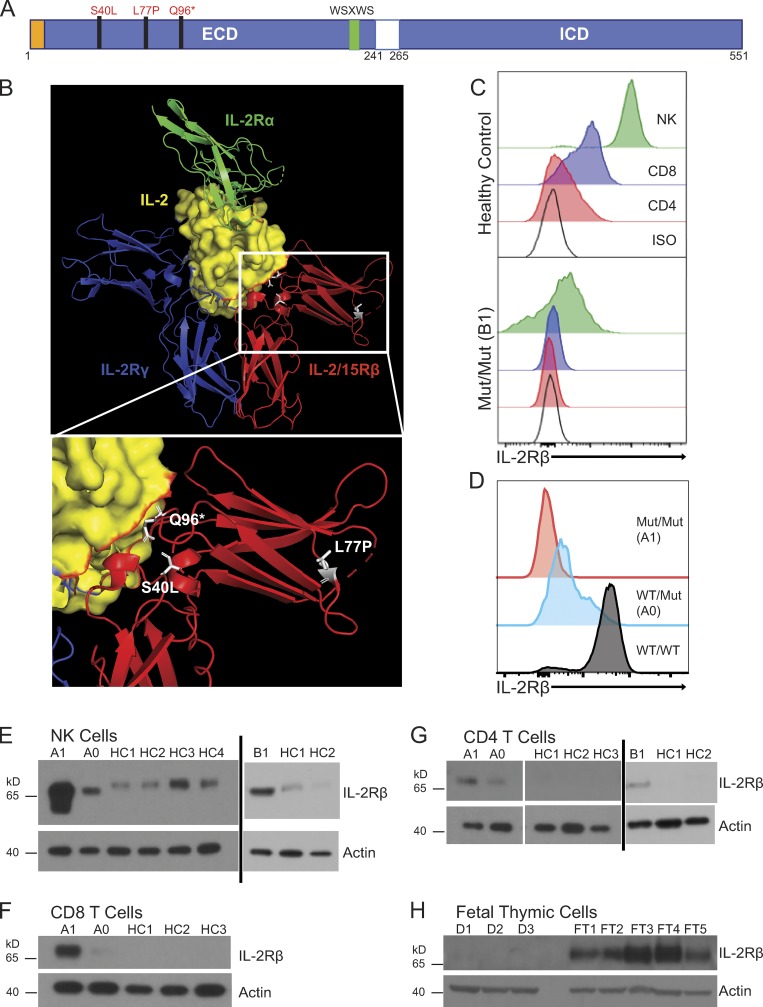
Figure 2.
IL2RB coding mutations cause IL-2Rβ surface receptor deficiency. (A) Schematic of intracellular (ICD) and extracellular domains (ECD) of the IL-2Rβ protein depicting the location of the three mutations in the ECD. The signal peptide is highlighted in orange, and the canonical WSXWS motif is highlighted in green. (B) Crystal structure of IL-2:IL-2R complex with the expanded view showing the position of the three mutations in white: L77P, S40L, and Q96*; (modified from PDB 2B5I, Wang et al., 2005). Red: IL-2/15Rβ; blue: IL-2Rγ; green: IL-2Rα; and yellow: IL-2 with IL-2Rβ interface colored in red. (C) Histogram of IL-2Rβ surface expression in CD3+ CD4+ (red), CD3+ CD8+ (blue), and CD3− CD56+ NK cells (green) and isotype control–stained cells (black) from healthy control (top panel) and patient B1 (bottom panel). (D) Histogram of IL-2Rβ surface expression in NK cells (CD3− CD56+; red, homozygous affected A1; blue, heterozygote healthy A0; black, healthy control). Data representative of four independent experiments. Mut, mutation. (E) Western blot of FACS-sorted CD3− CD56+ NK cells from A1, heterozygote parent (A0), B1, and four healthy controls (HC1–HC4). (F) Western blot of FACS-sorted CD3+ CD8+ T cells from A1, heterozygote parent (A0), and three healthy controls (HC1–HC3). (G) Western blot of FACS-sorted CD3+ CD4+ T cells from A1, heterozygote parent (A0), B1, and three healthy controls (HC1–HC3). (H) Western blot of fetal thymuses from kindred D (D1–D3) and five fetal thymic controls from 25-wk-old (FT3 and FT4) and 31-wk-old (FT1, FT2, and FT5). E–H, loading control: actin. Western blots (E–H) were repeated in triplicate.