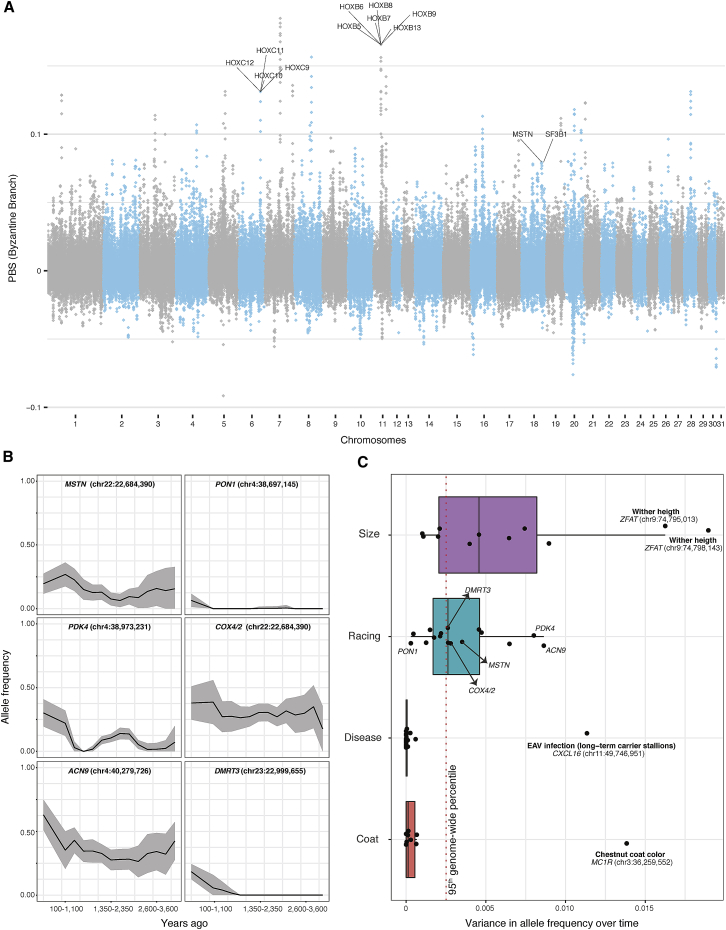
Figure 4.
Selection Targets through Time
(A) Population branch statistics (PBS) along the genome of 17 Byzantine horses, compared to 11 Gallo-Roman and 11 Deer Stone horses. The underlying tree topology consists of three groups with sufficient data and representing pre-C7th–C9th horses in Asia and Europe and post-C7th–C9th horses descending from Sassanid Persians. We used non-overlapping 50 kb genomic bins, and genes underlying enrichment for functional categories related to vertebral changes are indicated. These include Sf3b1 and seven HOXB/C genes. Hoxc11, Hoxb7, Hoxb13, and Hoxc12 are not annotated as related to vertebral modifications, but embedded within the two independent clusters of HOXB/C genes. The MSTN speed gene, one selection candidate in Byzantine horses, is also highlighted. See also Figure S4 and Tables S6 and S7 for further information.
(B) Temporal allele trajectories for six SNPs associated with racing performance and locomotion patterns.
(C) Variance in allele frequency over time for the 57 SNPs investigated, categorized according to their impact on racing performance, body conformation, diseases and coat-color variations. The red dashed line delimits the 95th percentile of the variance distribution obtained from all SNP positions segregating genome-wide. See also Figures S5 and S6 for the full list of the SNPs investigated.