Figure 1.
Poly(A) RNP Features Underpinning Pan2-Pan3 Deadenylation Activity
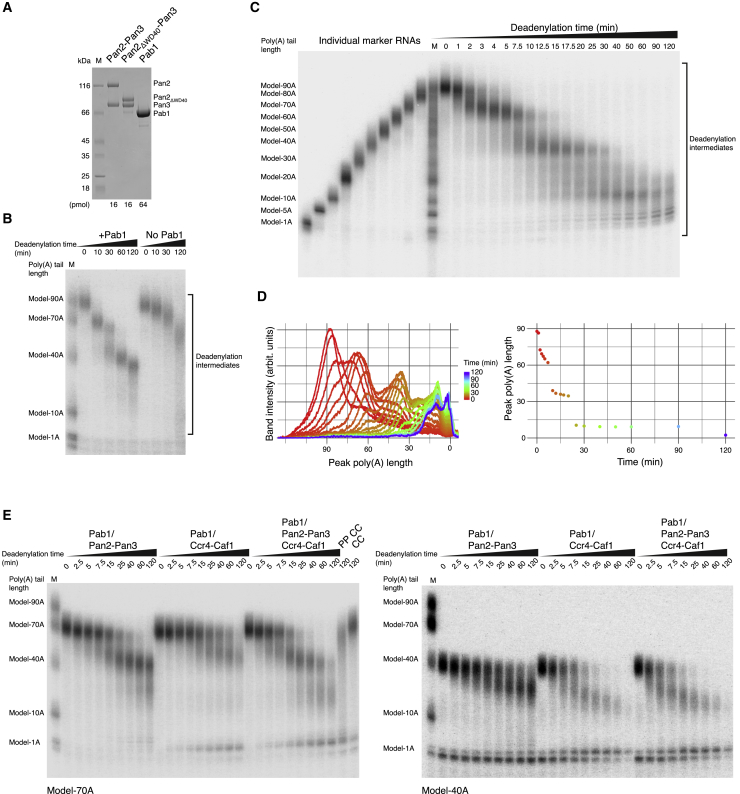
(A) Recombinant proteins used in deadenylation reactions. 12.5% SDS-PAGE gel visualized via Coomassie staining showing the purified recombinant proteins used in the assays: wild-type S. cerevisiae Pan2-Pan3 (Schäfer et al., 2014), Pan2ΔWD40-Pan3 (Figures 5, 6, and S6B), and Pab1 (Schäfer et al., 2014). M indicates the lane with size markers (in all gels of the manuscript).
(B) In vitro deadenylation activity of Pan2-Pan3 is stimulated by Pab1. A model-90A RNA was radioactively labeled at the 5′ end and incubated with wild-type Pan2-Pan3 in the absence or presence of Pab1 (in a 1:3 RNA:protein ratio, indicated by “no Pab1” and “+Pab1,” respectively; see also Figure S6B). Samples were withdrawn at indicated time points and the reactions were stopped. The samples were analyzed on a 6% denaturing Urea-PAGE gel followed by phosphorimaging.
(C) In vitro deadenylation of a yeast 90A RNP substrate by Pan2-Pan3 results in a phased poly(A) tail distribution. The same 5′-labeled model-90A RNA described in (B) was mixed with Pab1 (in a 1:3 RNA:protein ratio) and incubated with wild-type Pan2-Pan3 for 2 h. At indicated time points, samples were withdrawn and the reaction was stopped (see also Figure 5B). The samples of the deadenylation time course (right lanes) and the molecular weight markers (left lanes) were analyzed on a 6% denaturing Urea-PAGE gel followed by phosphorimaging. The recombinant proteins used in the assays are shown in (A).
(D) Quantitation of the in vitro deadenylation experiment reveals increased activity of Pan2-Pan3 on longer poly(A) RNPs. The raw data from (C) were quantified by densitometric analysis of each gel lane (left) and summarized by plotting the poly(A) length at peak intensity for each time point (right). See also Figure S1A and Table S2.
(E) Deadenylation time course of a model-70A RNP (1:2 RNA:Pab1 ratio, left panel) and a model-40A RNP (1:1 RNA:Pab1 ratio, right panel) upon addition of either Pan2-Pan3 or a Caf1-Ccr4 complex (Basquin et al., 2012) or both. The reactions were stopped at the indicated time points and analyzed on a 6% Urea-PAGE followed by phosphorimaging. On the left panel, the last two lanes mark 120-min-long control reactions in the absence of Pab1 with both Pan2-Pan3 and Caf1-Ccr4 (PP CC) or only with Caf1-Ccr4 (CC). See also Figure S1E.