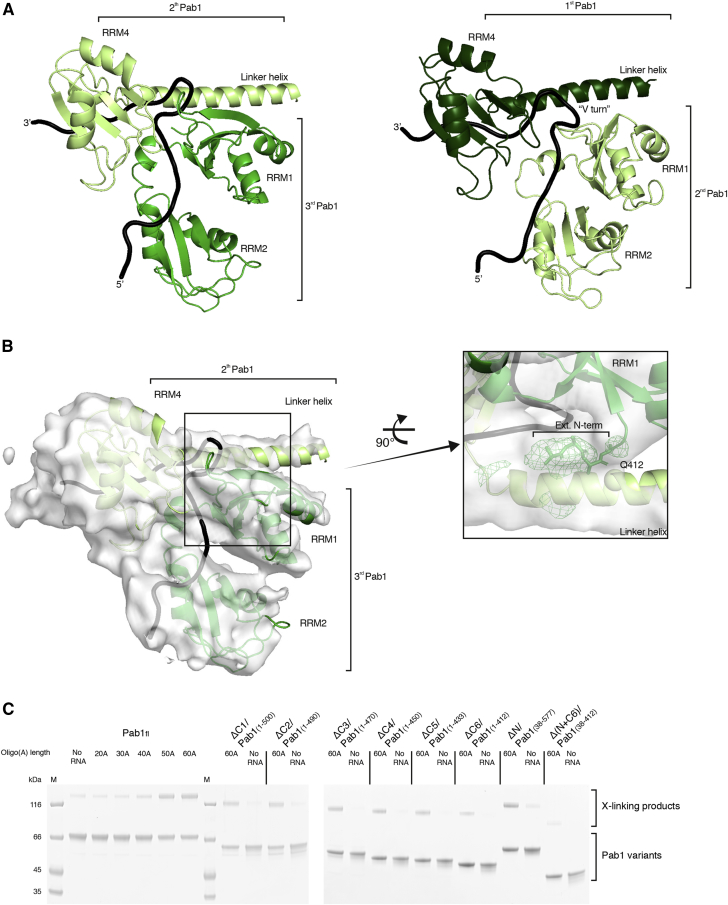
Figure S7.
The Pab1-Pab1 Oligomerization Interface, Related to Figure 5
(A) Juxtaposition of the first (right-hand panel) and the second (left-hand panel) Pab1-Pab1 oligomerization interface in cartoon representation and similar orientations. The 1st Pab1 is colored in dark green, the 2nd Pab1 in light green and the 3rd Pab1 in green and the RNA in black. The overall architecture of the two interfaces is very similar. The linker helix of the more 3′ Pab1 interacts in both cases with RRM1 of the more 5′ Pab1 forcing the RNA into a sharp roughly 110° turn (“V turn,” compare Figure 7A). The directionality of Pab1-Pab1 oligomerization is fixed by the defined polarity with which the poly(A) RNA binds the RRM1-RRM2 unit. This interaction provides most the RNA-binding affinity in the context of the full-length protein.
(B) Details of the 2nd Pab1-Pab1 interaction interface. The panel on the left shows the model with the corresponding area of density. On the right is a close up of the linker helix-RRM1 interface in density. A sphere indicates the approximate position of Q412. The main chain N-terminal to residue 38 of RRM1 (the leader sequence) is emphasized in licorice representation. Difference density for this N-terminal part is shown in green in a radius of 20 Å around the site.
(C) Ruthenium-based photo-crosslinking assay (photo-induced crosslinking of unmodified proteins or PICUP) of Pab1 constructs in the presence of varying length of RNA. On the left is the assay with full-length Pab1 in the presence of increasing length of oligo (A) followed by the experiment with C-terminal and N-terminal truncations of Pab1 in the presence and absence of 60A RNA. Crosslinking is most severely impaired in the construct lacking all residues N-terminal of amino acid 38 and all residues C-terminal to amino acid 412 in the linker helix. The approximate position of Q412 is indicated by a sphere in (B) and highlighted in the multiple sequence alignment in Figure S5B.