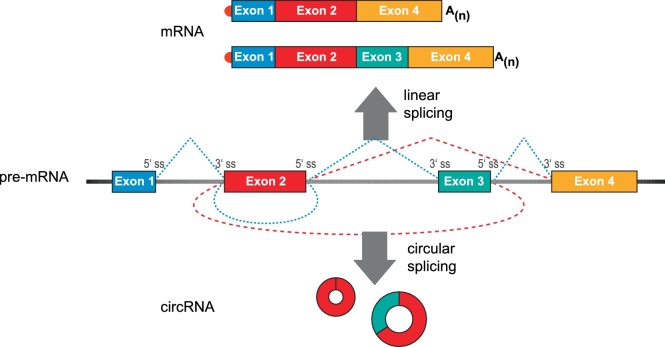
Fig. 2.
Biogenesis of circular RNAs (circRNAs). Schematic representation of the biogenesis of linear mRNA and circular RNA. During canonical splicing, introns are removed and exons are joined with each other, generating either a single mRNA from the pre-mRNA (constitutive splicing) or several splice variants (alternative splicing). CircRNAs are generated by an alternative splicing mechanism, also referred to as backsplicing, in which a 5′ splice site (5′ ss) is joined to an upstream 3′ splice site (3′ ss) instead of a downstream 3′ ss. Different splice variants can be generated by alternative backsplicing resulting in single- or multi-exonic circular RNAs (circRNAs). Exons are depicted as colored boxes and introns as solid lines. The 5′ cap structure of mRNA is shown as red dots and the 3′ poly(A) tail as A(n). Constitutive (blue) and alternative splicing (red) is indicated by dashed lines.