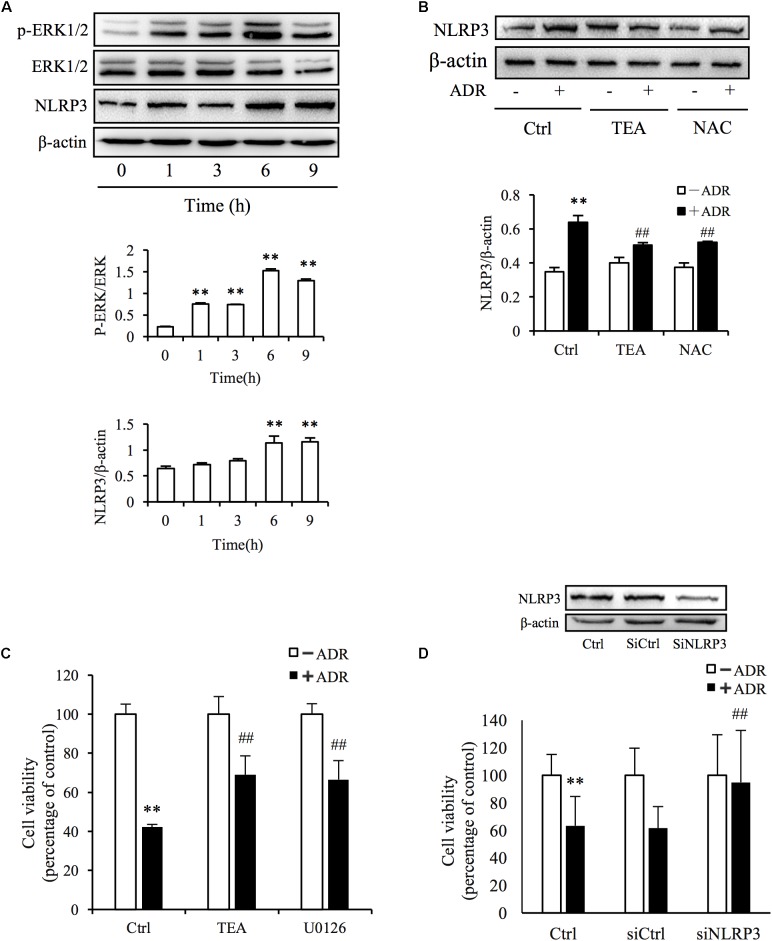
FIGURE 6.
ADR induces oxidative stress-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation. (A) Induction of ERK1/2 phosphorylation and NLRP3 protein levels by ADR. NRK-52E cells in 12-well plates were incubated with ADR for 1, 3, 6, and 9 h, respectively. Statistical analyses of phosphorylated ERK1/2 and NLRP3 are shown at the bottom (means ± SD, n = 3; ∗∗P < 0.01 versus Ctrl). (B) Effects of TEA and NAC on NLRP3 induced by ADR. NRK-52E cells in 12-well plates were pretreated with TEA or NAC for 1 h and incubated with ADR for 9 h. Statistical analyses of NLRP3 are shown at the bottom (means ± SD, n = 3; ∗∗P < 0.01 versus Ctrl; ##P < 0.01 versus ADR in Ctrl). (C) Effects of TEA and U0126 on cell viability. NRK-52E cells in 96-well plates were pretreated with TEA (100 μg/mL) or U0126 (20 μM) for 1 h and challenged with ADR for 24 h. Cell viability was evaluated by CCK-8 assay. Data are expressed as percentages of living cells versus control (means ± SD, n = 5). ∗∗P < 0.01 versus control; ## P < 0.01 versus ADR in Ctrl. (D) Effects of NLRP3 siRNA on ADR-induced cell injury. NRK-52E cells were transfected with either NLRP3 siRNA or control siRNA for 24 h. The transfected cells were incubated with ADR for 24 h. Cell viability was evaluated using a CCK-8 assay. Data are expressed as the percentages of living cells compared with the siRNA controls (means ± SD, n = 4; ∗∗P < 0.01 versus siRNA control; ## P < 0.01 versus ADR in Ctrl).