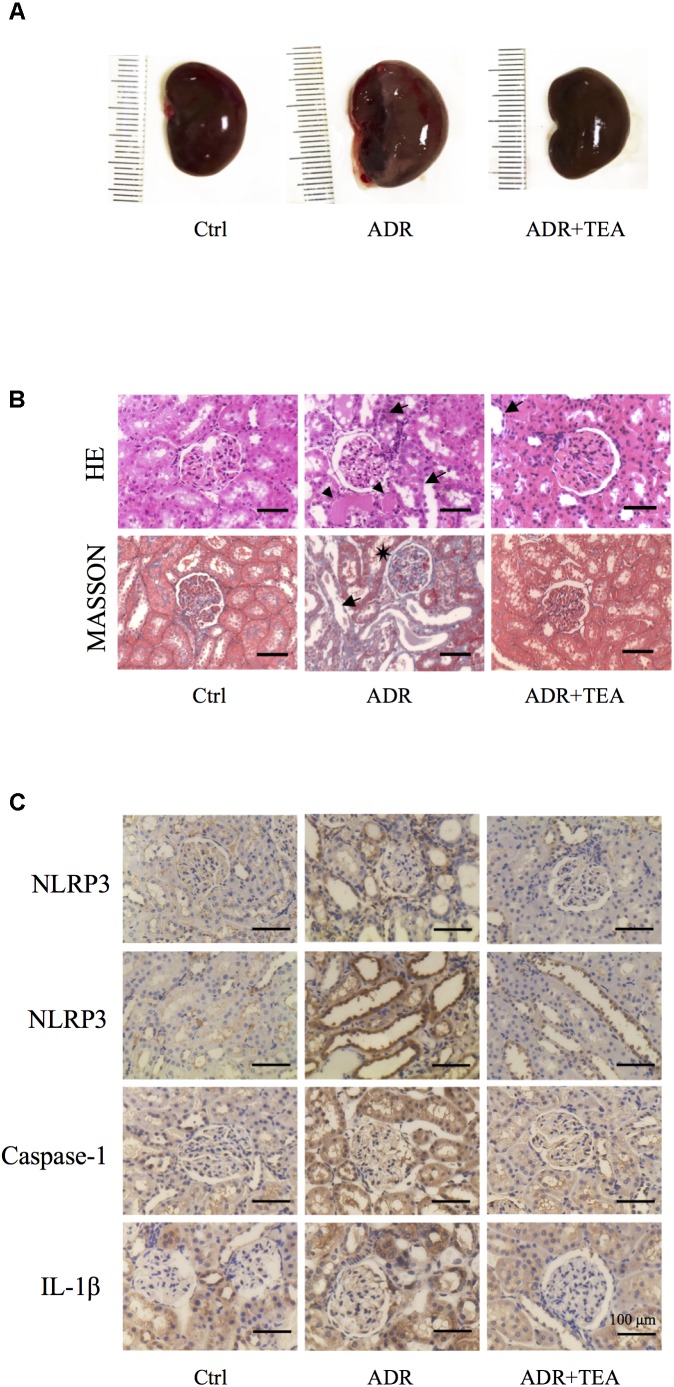
FIGURE 9.
TEA improves renal pathology in rats with Adriamycin nephropathy. (A) Macroscopic morphology of the kidneys. (B) Hematoxylin and Eosin staining: Renal tubular epithelial cells in the normal group were in alignment and had normal shapes. In the ADR group, the renal tubular epithelial cells were shed, and some of the bare membranes were visible, while some of them had regenerated (arrows). Protein casts are indicted as (Δ). Granular degeneration can be seen in proximal tubular cells. Renal tubular epithelial cells were detached (arrows) in the treatment group, which was at a lower level compared with the ADR group. Masson staining: Capillary vasospasm and buccal segmental adhesion (∗) were detected in the Adriamycin group. Renal tubular epithelial cells were detached, and bare membranes (arrow) were visible. There was no obvious fibrosis in the renal interstitium. Scale bar: 100 μm. (C) Representative images of sections assayed by immunohistology using NLRP3, Caspase 1, and IL-1β antibody. Scale bar: 100 μm.