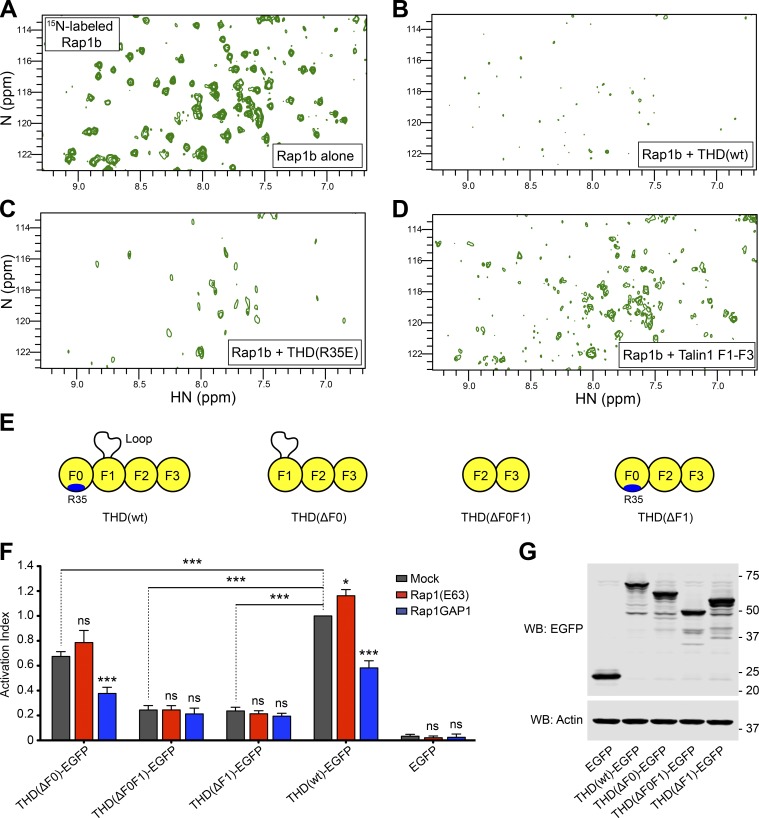
Figure 1.
THD contains a second Rap1-binding site. (A–D) 2D 1H,15N-sfHMQC spectra of 100 µM 15N-labeled Rap1b. (A) Free Rap1b. (B) Rap1b with 250 µM THD(wt). The broadening of Rap1 resonances in the presence of THD indicates binding. (C) Rap1b with 250 µM THD(R35E). The broadening indicates the presence of a second Rap1-binding site. (D) Rap1b with 250 µM THD(ΔF0). The intermediate broadening indicates the second Rap1-binding site outside the F0 domain. (E) THD constructs used in F and G. (F) A5 cells stably expressing αIIbβ3 integrin were transfected with cDNA encoding THD-EGFP in combination with Rap1(Q63E) or Rap1GAP1. Integrin activation was assayed by binding of PAC1 to EGFP-positive cells. Transfection of EGFP alone was used as control. Bar graphs represent mean ± SEM of four independent experiments and normalized to THD(wt)-EGFP + mock. Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-test. Each condition was compared with the respective mock control. *, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001. (G) WB of THD-EGFP expression. Actin was used as a loading control.