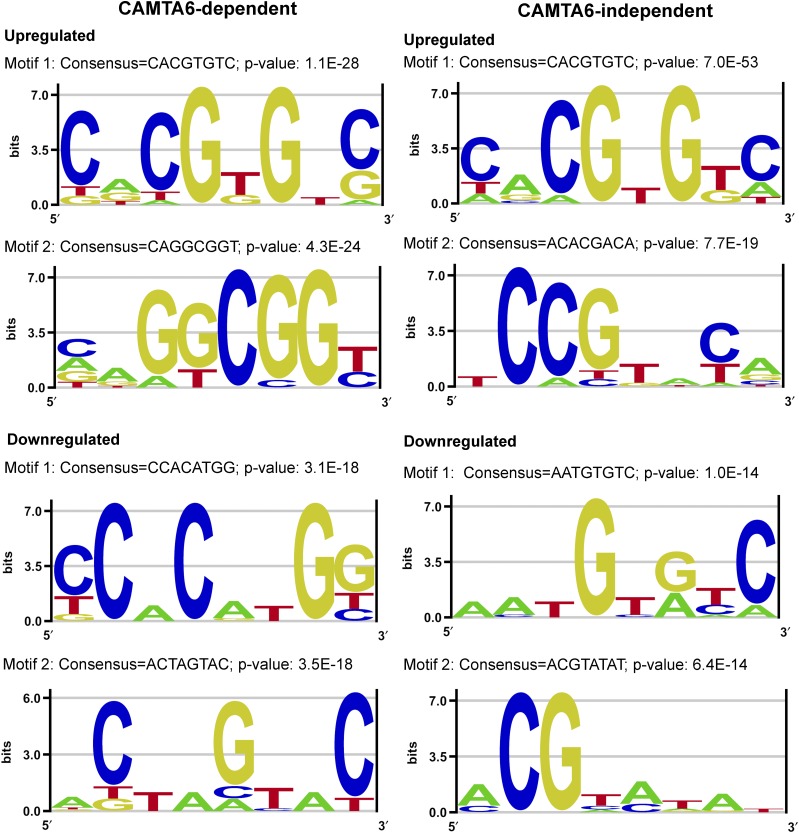
Figure 7.
Highly represented sequence motifs in the promoters of differentially expressed genes in the CAMTA6-dependent and CAMTA6-independent groups. Promoter analyses of differentially expressed genes in the CAMTA6-dependent and CAMTA6-independent groups were performed using the Amadeus-Allegro software (http://acgt.cs.tau.ac.il/allegro/download.html) on the 1,000 bp genomic sequences upstream of the transcription start sites of the corresponding genes. Motifs of eight bases were derived from the JASPAR regulatory motif database. The recommended statistically significant P value is 1E−20 or less. Left, CAMTA6-dependent genes. In the up-regulated group, motif 1 with a consensus CACGTGTC and a P value of 1.1E−27 represents an ABRE- and CAMTA-binding site. Motif 2 with a consensus CAGGCGGT/C and a P value of 4.3E−24 represents a GCC-box, DRE-like, which is a binding motif of the DREB family TFs. This box is also known as an ethylene-responsive element (Solano et al., 1998). In the down-regulated differentially expressed CAMTA6-dependent genes, motif 1 with a consensus CCACATGG and a P value of 3.1E−18 represents a MYC recognition site in the promoters of the dehydration-responsive gene rd22 and in the DREB1A promoter and ICE1-binding site. Motif 2 with a consensus ACTAGTAC and a P value of 3.5E-18 represents SORLREP1, a motif involved in light-regulated gene expression (Hudson and Quail, 2003). Right, CAMTA6-independent genes. Promoter analysis in the up-regulated genes revealed the classical ABRE (with a consensus CACGTGT/GC), which also represents the ABRE/CAMTA motif, the major motif in the up-regulated genes (P value of 7.0E−53). The major motif in the down-regulated salt-responsive CAMTA6-independent genes has a consensus AATGTG/AT/CC (P value of 1.0E−14), but the identity of this motif could not be verified and its occurrence is not considered statistically significant.