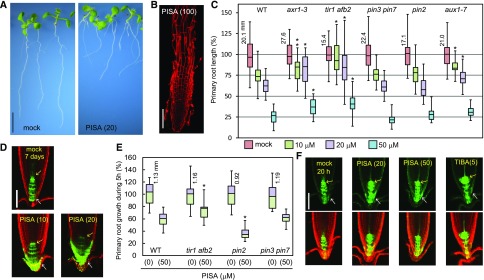
Figure 4.
The effects of PISA on root elongation and auxin distribution in the root tip. A, Wild-type (WT) seedlings cultured for 7 d with PISA. Bar = 5 mm. B, Wild-type root cultured with 100-μm PISA . Root was counterstained with propidium iodide. Bar = 100 μm. C, The primary root length of Arabidopsis wild-type and auxin mutants (axr1-3, tir1 afb2, pin3 pin7, pin2/eir1-1, and aux1-7) cultured for 7 d on vertical plate containing PISA. Relative root length is shown as the percentage of that in mock-treated plants (100%). The actual length (millimeter) of mock-treated roots is indicated. Statistical significance was assessed by Welch’s two-sample t test between wild type and mutants. Asterisks indicate significant differences (n = 32–40, **P < 0.05, *P < 0.01). D, The GFP expression of DR5::GFP in roots cultured vertically with PISA for 7 d. Arrows indicate QC (yellow) and lateral root cap (white). Bar = 100 μm. E, The primary root growth of Arabidopsis wild type and auxin mutants over 5 h on vertical plates containing PISA. The actual length (mm) of mock-treated roots is indicated, which was set to 100%. Asterisks indicate significant differences (n = 14–17, *P < 0.01). F, The GFP expression of DR5::GFP cultured vertically with PISA and TIBA for 20 h. The values in parentheses represents the concentration of chemicals (micromolar). Bar = 100 μm.