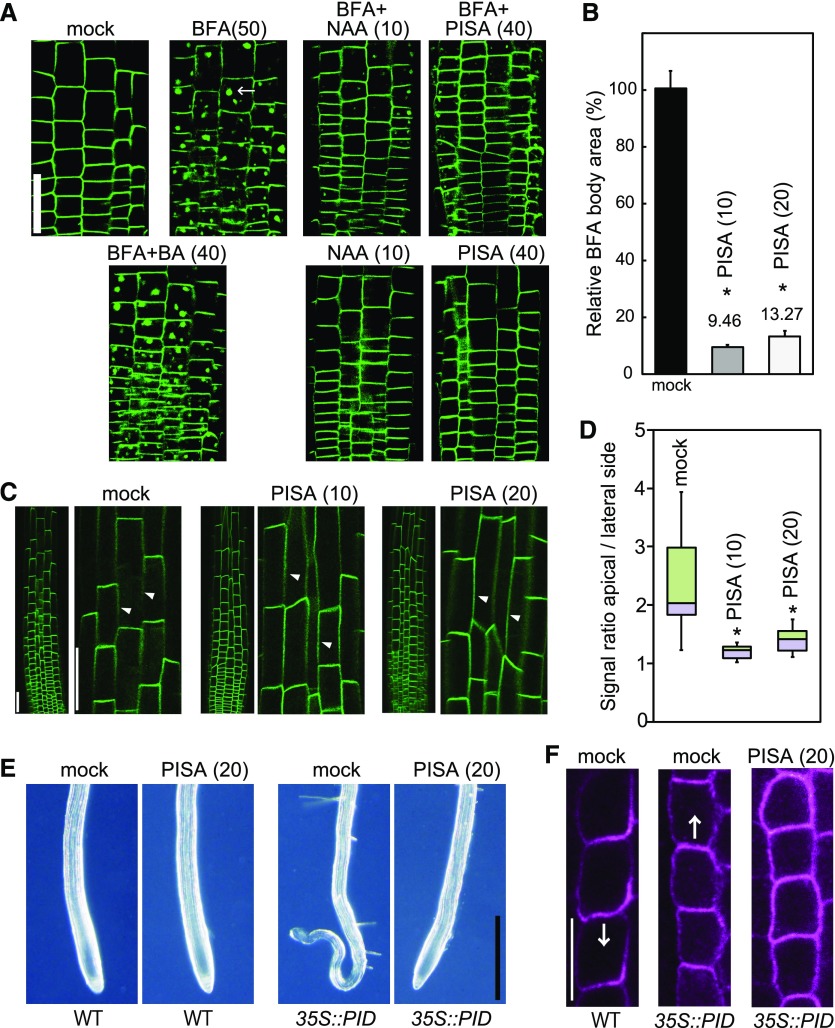
Figure 8.
Effects of PISA on PIN internalization from the PM. A and B, Effect of PISA on the BFA body formation of PIN2-GFP. Five-d–old proPIN2::PIN2-GFP seedlings were incubated for 30 min in liquid GM medium containing PISA, benzoic acid (BA) and NAA, and then BFA was added to the medium. Seedlings were then incubated for additional 60 min. BFA induced PIN2-GFP-marked BFA bodies. The area of BFA body was measured and the area in BFA-treated seedlings (n = 25–40, *P < 0.01) was adjusted to 100%. The value of the area is shown the means ± sd in (B). Bar = 50 μm. C and D, Effect of PISA on the internalization of PIN2-GFP. Five-d–old proPIN2::PIN2-GFP seedlings were incubated for 12 h with PISA. The fluorescence intensity of the apical and lateral sides of cells in the root (n = 18–20, *P < 0.01) were quantified and the fluorescent signal rate (apical side/lateral side) is shown as the means ± sd in (D). The values in parentheses represent the concentration of chemicals (micromolar). Bar = 50 μm. Arrowheads show lateral cell side. E, Effects of PISA on a collapse of the primary root meristem. Five-d–old root tips of wild-type (WT) and 35S::PID plants grown vertically on agar plates containing PISA. Bar = 500 μm. F, Effects of PISA on PIN1 localization in the endodermis of wild-type and 35S::PID roots. Immunolocalization of PIN1 after treatment with PISA for 4 h. Bar = 10 μm. Arrows indicate the direction of IAA transport by PIN1.