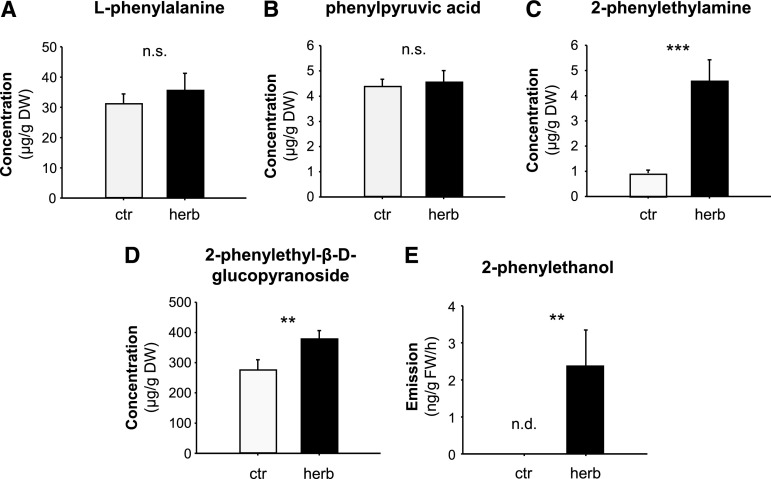
Figure 2.
Herbivore-damaged leaves of P. trichocarpa accumulate and release Phe-derived metabolites. A–E, The accumulation of l-Phe (A), phenylpyruvic acid (B), 2-phenylethylamine (C), and 2-phenylethyl-β-d-glucopyranoside (D), and the emission of 2-phenylethanol (E) were analyzed in L. dispar damaged (herb) and undamaged control (ctr) leaves. Plant material was extracted with methanol and analyzed via LC-MS/MS (A–D). Volatiles were collected for 8 h and analyzed via GC-FID (E). Means ± se are shown (A–D, n = 10; E, n = 9). Asterisks indicate statistical significance as assessed by Student’s t test or Mann-Whitney Rank Sum tests. l-Phe (P = 0.530, t = −0.64); phenylpyruvic acid (P = 0.772, t = −0.294); 2-phenylethylamine (P < 0.001, T = 55); 2-phenylethyl-β-d-glucopyranoside (P = 0.011, T = 71); 2-phenylethanol (P = 0.005, T = 58.5). DW, dry weight; FW, fresh weight; n.s., not significant; n.d., not detected.