Figure 1.
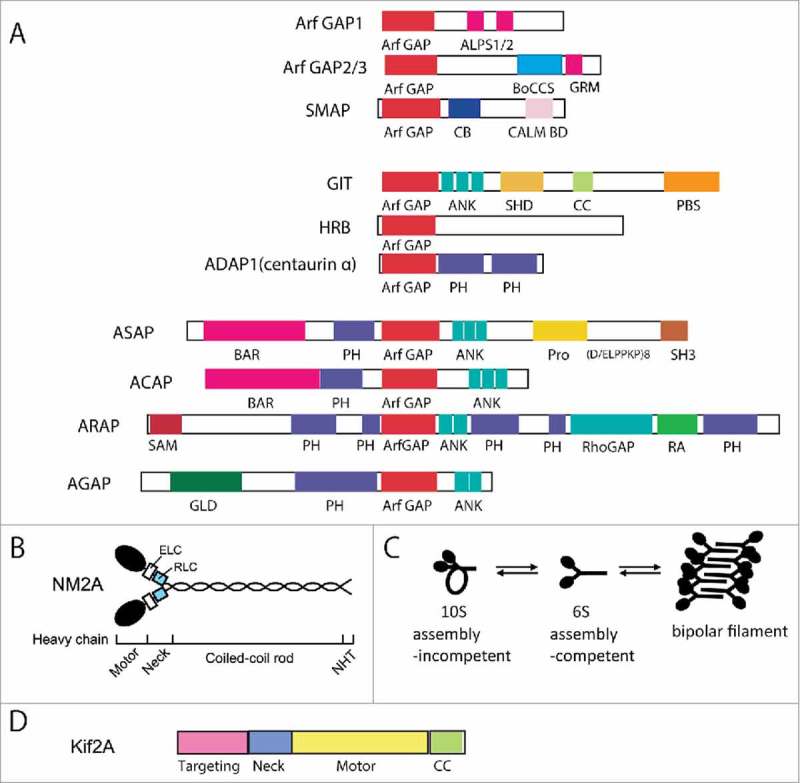
Domain structures of Arf GAPs and associated motor proteins. (A) Domain structures of the human Arf GAP subfamilies are depicted. Abbreviations are: ALPS, ArfGAP1 lipid-packing sensor; ArfGAP, ArfGAP domain; ANK, ankyrin repeat; BAR, Bin/Amphiphysin/Rvs; BoCCS, binding of coatomer, cargo and SNARE; CALM, CALM binding domain; CB, clathrin-box; CC, coiled-coil; FG repeats, multiple copies of the XXFG motif; GLD, GTP-binding protein-like domain; GRM, Glo3 regulatory motif; PBS, Paxillin binding site; PH, pleckstrin homology domain; Pro(PxxP)3, cluster of 3 Proline-rich (PxxP) motifs; Pro(D/ELPPKP)8, 8 tandem Proline-rich (D/ELPPKP) motifs; RA, Ras association motif; RhoGAP, RhoGAP domain; SAM, sterile α-motif; SH3, Src homology 3 domain; SHD, Spa-homology domain. Adapted from Kahn et al. 2009. (B) Domain structure of Nonmuscle myosin 2A. NM2A is composed of 2 heavy chains, 2 essential light chains (ELCs) and 2 regulatory light chains (RLCs). Each heavy chain contains a motor head domain, a neck region, a coiled-coil rod and a non-helical tail (NHT). (C) Conformations of NM2. D. Domain structure of Kif2A.
