Figure 2.
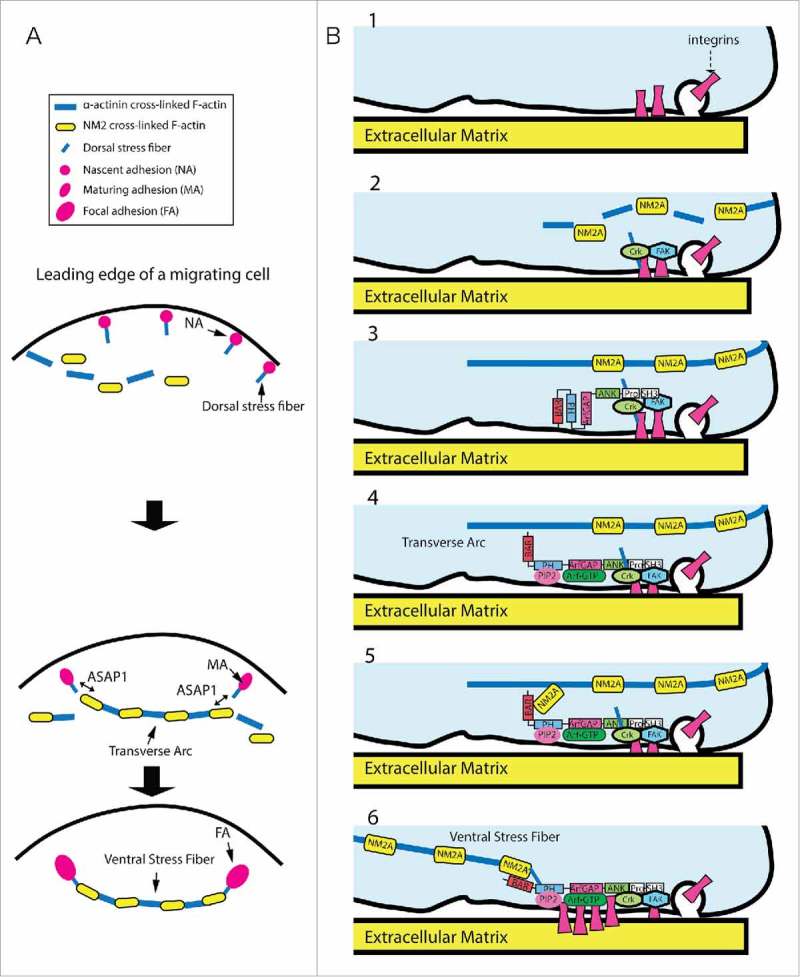
Model for ASAP1 function through NM2A to control maturation of stress fibers and associated integrin adhesions. (A) Hypothetical model for assembly of contractile stress fibers. Transverse arcs are assembled by endwise joining of NM2 and α-actinin cross-linked F-actin. The dorsal stress fibers emanating from integrin adhesions attach to arcs to form a continuous contractile stress fiber networks. The network contracts and flow toward the cell center. Ventral stress fibers are generated from transverse arcs located between 2 dorsal stress fibers. (B) ASAP1 couples assembly of actomyosin stress fibers to maturation of FAs. 1. Integrins are delivered to the cell surface and make contact with the extracellular matrix resulting in their activation. 2. Activated integrins recruit several proteins such as talin and paxillin, which recruit additional proteins including Crk and FAK. 3. ASAP1 is recruited to the nascent adhesionsvia binding of its proline rich domain to Crk and binding of its SH3 domain to FAK. 4. ASAP1 associates with PIP2 and Arf•GTP that are enriched in the forming adhesions. 5. PIP2 and Arf•GTP-bound ASAP1 interacts with NM2A (note that the roles of PIP2 and Arf in NM2A association are purely speculative, see text), stabilizing association of NM2A with actin filaments at the junction between dorsal stress fibers and transverse arcs. 6. Contractility of actomyosin stress fibers drives enlargement and maturation of the integrin adhesion.
