Figure 1.
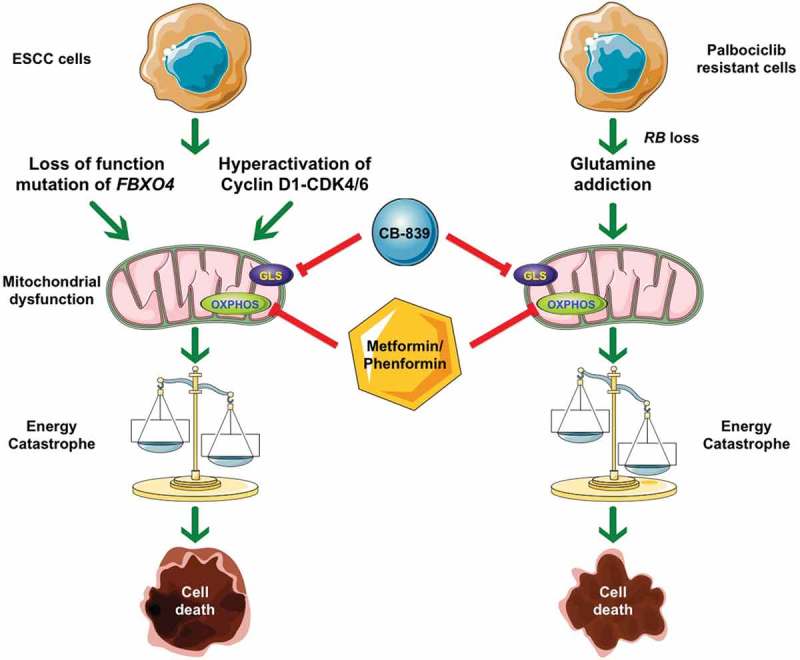
Molecular mechanisms of combined treatment with CB-839 and metformin/phenformin. 1) Loss of function mutations in F-Box Protein 4 (FBXO4) or hyperactivation of the Cyclin D1 (CCND1)-cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 (CDK4/6) leads to mitochondrial dysfunction and glutamine-addiction. Taking advantage of these metabolism characteristics, targeting both glutaminase (GLS) and oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) causes the imbalance between energy production and consumption, thereafter, energetic catastrophe, and finally cell death. 2) Palbociclib-resistant cells demonstrate RB transcriptional corepressor 1 (RB) loss that drives glutamine-addiction; moreover, these cells are more sensitive to combined treatment when compared with their parental counterparts. ESCC: esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
