Figure 4. FAAH-4 is inhibited by JZL184.
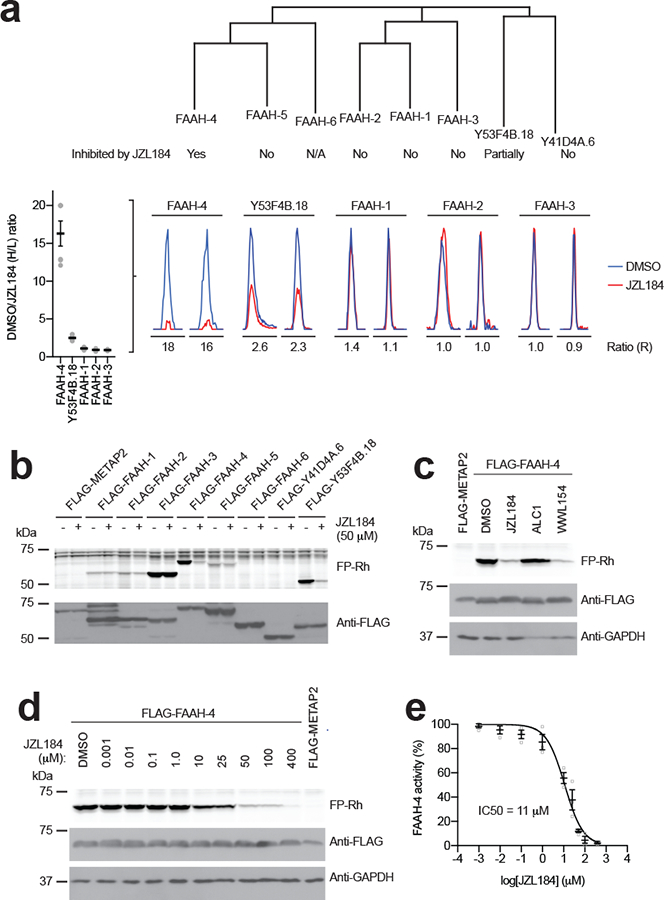
(a) Dendrogram showing the C. elegans amidase family and designating the sensitivity of individual amidases to JZL184. FAAH-6 is marked as N/A because this protein is missing a conserved serine in the amidase signature Ser-Ser-Lys catalytic triad and is therefore considered an inactive member of the family. Images below the dendrogram show representative MS1 traces for inhibition of the indicated amidases in JZL184-treated C. elegans (as determined by MS-based competitive ABPP). Data represent the mean of median ratios + s.e.m. for peptides quantified for each protein (n = 4 independent experiments). (b) Gel-based competitive ABPP showing cross-reactivity of recombinant amidases with JZL184. Only recombinant FAAH-4 and Y53F4B.18 showed evidence of inhibition by JZL184, consistent with the MS-based competitive ABPP analysis of JZL184-treated C. elegans (Fig. 3a). Note that FAAH-6 is missing a conserved serine in the amidase signature Ser-Ser-Lys catalytic triad and is therefore considered an inactive member of the family. (c) Gel-based competitive ABPP results showing inhibition of recombinant FAAH-4 by JZL184 and WWL154 but not ALC1 (50 μM of each compound, 30 min treatment). Full-length gels containing cropped gel data are shown in Supplementary Fig. 7. (d, e) Concentration-dependent inhibition of recombinant FAAH-4 by JZL184 as measured by gel-based ABPP. For e, data represents mean ± s.e.m. (n = 3 independent experiments). Full-length gels containing cropped gel data are shown in Supplementary Fig. 7. For b-d, C. elegans SHs or control protein (METAP2) were recombinantly expressed by transient transfection in HEK-293T cells. For b-d, data are representative of 3 independent experiments.
