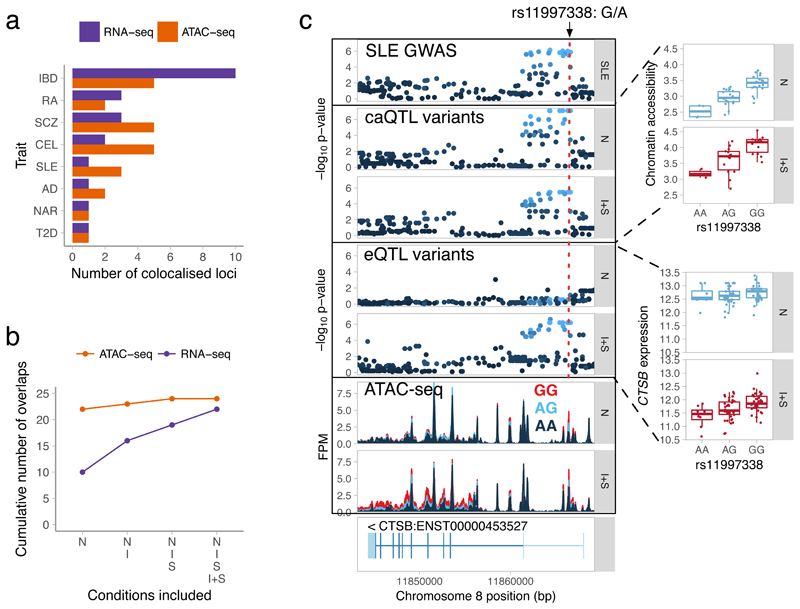
Figure 4. Identifying eQTLs and caQTLs that colocalise with complex disease risk loci.
(a) Total number of colocalised GWAS hits identified for each trait across the four conditions. (b) Cumulative number of colocalised GWAS hits identified by starting with overlaps in the naive condition and sequentially adding IFNγ, Salmonella and IFNγ + Salmonella conditions. (c) Colocalisation between an SLE GWAS hit (rs11997338), chromatin accessibility and CTSB gene expression (n = 84 independent donors) before and after IFNγ + Salmonella stimulation. The caQTL results are based on n = 42 (naive) and n = 31 (IFNγ + Salmonella) independent donors. FPM, fragments per million. Disease acronyms: SLE, systemic lupus erythematosus; IBD, inflammatory bowel disease; RA, rheumatoid arthritis; SLE, systemic lupus erythematosus; AD, Alzheimer’s disease; SCZ, schizophrenia; T2D, type 2 diabetes; NAR, narcolepsy; CEL, celiac disease. The -log10 p-values on panels c were calculated using FastQTL55. Box plots show the median (center line) and the 25th and 75th percentiles (box edges), with whiskers extending to 1.5 times the interquartile range.