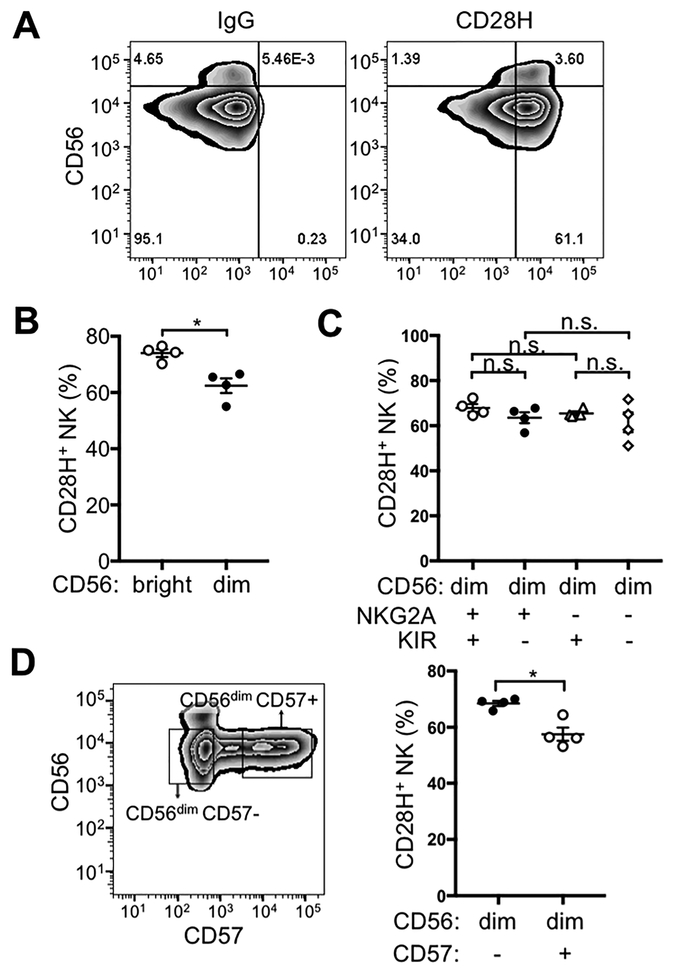
Figure 1. CD28H expression on human NK cells.
(A) Freshly isolated NK cells were stained for CD56 and CD28H with fluorophore-conjugated mAbs. An isotype control (IgG) for CD28H is shown in the left panel. (B) Expression of CD28H was compared between CD56bright and CD56dim NK cells. Each symbol represents an independent donor (n=4). (C) Expression of CD28H in different CD56dim subsets defined by KIR and NKG2A expression. Receptors of the KIR family were stained using a cocktail of PE-conjugated antibodies (EB6, GL183 and DX9). Each symbol represents an independent donor (n=4) (D) CD28H expression on CD56dimCD57– and CD56dimCD57+ NK cells. Each symbol represents an independent donor (n=4). All data are presented as the mean ± SEM. *P<0.05, n.s. not-significant (Mann-Whitney test, two-tailed). All experiments have been repeated at least twice.