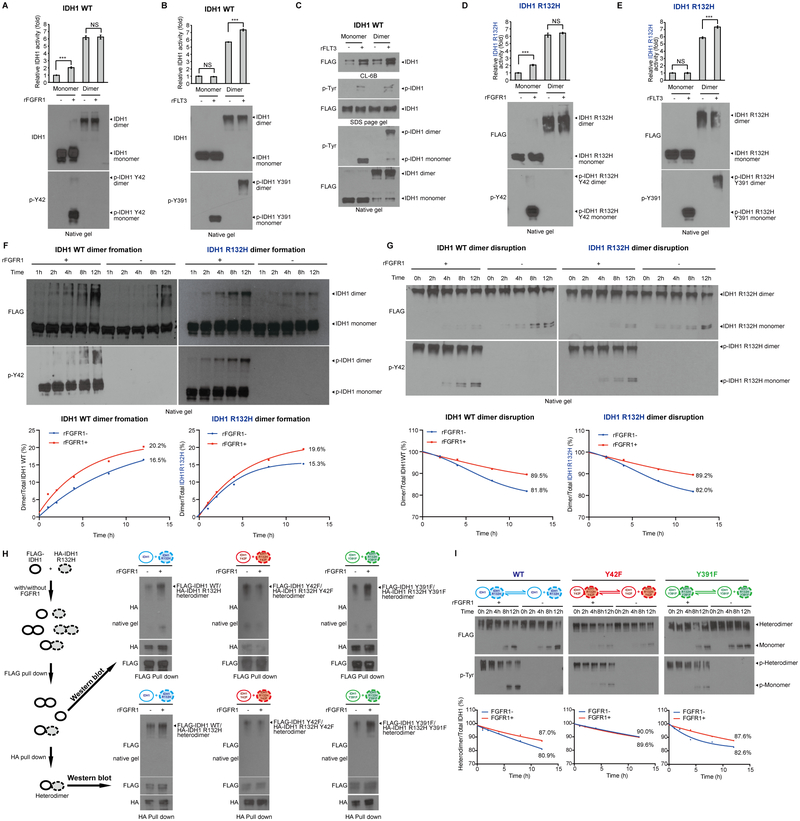
Figure 5.
Activation of IDH1 is enhanced by distinct oncogenic tyrosine kinase cascades through direct and indirect phosphorylation. A-B, Purified IDH1 WT monomer and dimer were treated with recombinant active Group I tyrosine kinase FGFR1 (A) or Group II tyrosine kinase FLT3 (B), respectively, followed by IDH1 WT enzyme activity (upper panels). Monomeric and dimeric IDH1 protein levels and tyrosine phosphorylation at Y42 and Y391 of IDH1 were detected by Western blotting using native PAGE (lower panels). C, Purified IDH1 WT monomer and dimer were treated with or without recombinant active Group II tyrosine kinase FLT3, followed by incubation with Blue Sepharose CL-6B beads that mimic NADP+ binding. Bound monomeric and dimeric IDH1 proteins and tyrosine phosphorylation of IDH1 were determined by Western blotting using native PAGE. D-E, Purified IDH1 R132H monomer and dimer were treated with recombinant active Group I tyrosine kinase FGFR1 (D) or Group II tyrosine kinase FLT3 (E), respectively, followed by IDH1 R132H enzyme activity (upper panels). Monomeric and dimeric IDH1 R132H protein levels and tyrosine phosphorylation at Y42 and Y391 of IDH1 R132H were detected by Western blotting using native PAGE (lower panels). F-G, Purified monomeric IDH1 and IDH1 R132H (F) or purified dimeric IDH1 and IDH1 R132H (G) were treated with recombinant active Group I tyrosine kinase FGFR1 in a time dependent manner, followed by native PAGE. Spontaneous dimer formation (F), monomer conversion (G), and tyrosine phosphorylation levels at Y42 of IDH1 and IDH1 R132H were detected by Western blotting. Lower panels show density analysis of corresponding bands to assess dimer formation and monomer conversion in Western blotting. The ratio between homodimers and total IDH1 WT or mutant proteins were quantitatively determined based on density analyses of the Western blotting. H, Left panels: Purified monomers of FLAG-tagged IDH1 and HA-tagged IDH1 R132H were mixed in the presence and absence of recombinant FGFR1, and different monomers and dimers in the mixture were indicated (top two panels, respectively). FLAG pull down was performed to enrich FLAG-IDH1 containing monomers and homo- and hetero-dimers, (middle panel), which were either applied to native gel followed by Western blotting (Figure 5H, upper right), or to HA pull down to further purify the heterodimers (bottom left). Upper right: FLAG-IDH1/HA-R132H heterodimers were detected by HA blotting in native gels. Lower right: FLAG-IDH1/HA-R132H heterodimers purified by sequential FLAG-HA pull downs were detected by FLAG blotting in native gels. I, Purified FLAG-IDH1/HA-IDH1 R132H heterodimers form by non-phosphorylated or FGFR1-phosphorylated monomers of FLAG-IDH1 and HA-IDH1 R132H variants spontaneously disrupt to form monomers in a time dependent manner. Heterodimers and monomer conversions as well as tyrosine phosphorylation levels of dimeric and monomeric proteins were detected by Western blotting. The ratio between heterodimers and total IDH1 proteins were quantitatively determined based on density analyses of the Western blotting.
The error bars represent mean values ±SD from three replicates of each sample (***: p<0.001; ns: not significant); Data are mean ± SD; p values were obtained by a two-tailed Student’s test.