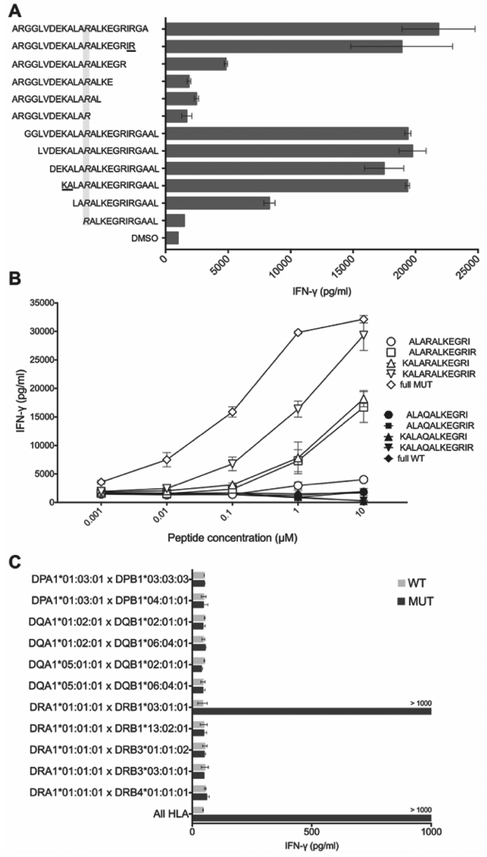
Figure 3. Determination of minimal epitope and HLA restriction element for CTBP1Q277R-TCR.
(A) CTBP1Q277R-TCR-transduced T cells were co-cultured with autologous EBV-B cells pulsed with serial two-amino acid truncations of CTBP1Q277R 25-mer. IFN-γ concentration was determined by ELISA. Top 6 sequences on the y axis represent truncations from the C-terminus, and the bottom 6 from the N-terminus of CTBP1Q277R 25-mer. Grayed area highlights the Q277R mutation; underlined amino acids delineate the potential minimal epitope. (B) Transduced T cells were co-cultured with autologous EBV-B cells pulsed with CTBP1Q277R 25-mer, 13-mer identified in (A), and three additional truncations of the latter (white dots). Corresponding WT peptides were used as a control (black dots). IFN-γ concentration was determined by ELISA. (C) COS-7 cells, transfected with combinations of plasmids encoding all paired MHC class II molecules identified in Patient 1, were pulsed for 2 hours with WT or CTBP1Q277R (MUT) peptide and co-cultured with CTBP1Q277R-TCR-transduced T cells. Results of IFN-γ ELISA are shown. For (A-C), a representative of two independent experiments is shown. Data represents average reads from two duplicate co-culture wells; error bars represent SD.