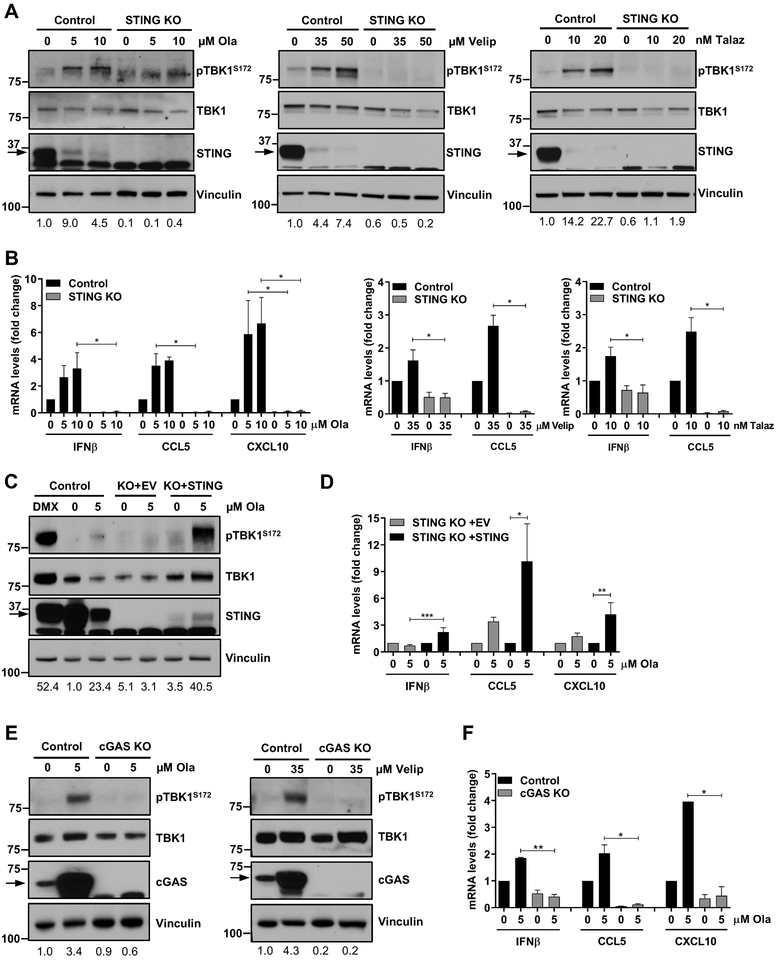
Figure 5. STING or cGAS depletion abolishes olaparib-induced proinflammatory signaling.
(A-B) Murine K14 CRISPR/Cas9 control or STING knockout (STING KO) cells were treated with DMSO (0 μM) or the indicated doses of olaparib, veliparib or talazoparib for 72h and subjected to immunoblotting or qPCR. STING depletion, as shown by immunoblotting for total STING levels, abolishes PARP inhibitor-induced TBK1 phosphorylation and upregulation of IFNβ, CCL5 and CXCL10 mRNA levels, as measured by immunoblotting and qPCR, respectively. Arrows on the blots indicate specific bands and markers indicate MW (kDa). Error bars represent SEM of 3 independent experiments. Statistical analyses were performed using Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s post-hoc test. (C-D) K14 CRISPR/Cas9 control, STING KO with empty vector (KO+EV) or STING KO with STING-repletion (KO+STING) cells were treated with DMSO or olaparib for 72h and subjected to immunoblotting or qPCR. DMXAA (DMX; 10 μM) was used as a positive control. STING repletion in KO cells, as shown by immunoblotting for total STING levels, rescues olaparib-induced TBK1 phosphorylation and induction of IFNβ, CCL5 and CXCL10 mRNA expression. Error bars represent SEM of 3 independent experiments. Statistical analyses were performed using Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s post-hoc test. (E-F) K14 CRISPR/Cas9 control or cGAS KO cells were treated with the indicated doses of olaparib or veliparib for 72h and subjected to immunoblotting or qPCR. cGAS depletion, as shown by immunoblotting for cGAS levels, abolishes PARP inhibitor-induced TBK1 phosphorylation and upregulation of IFNβ, CCL5 and CXCL10 mRNA levels, as measured by immunoblotting and qPCR, respectively. Error bars represent SEM of 3 independent experiments. Statistical analyses were performed using Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s post-hoc test.