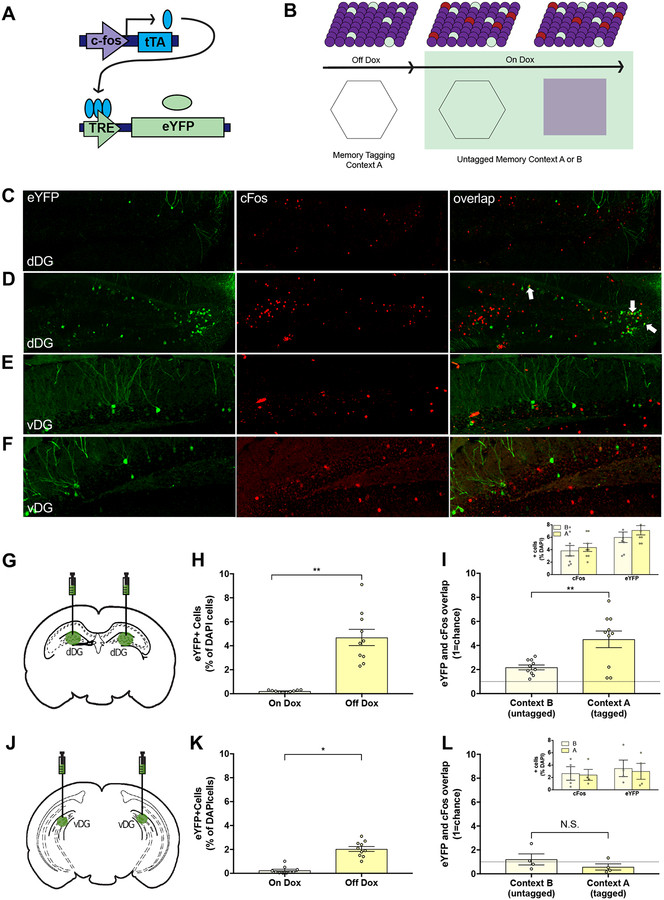
Figure 1. Activity-dependent and inducible expression of enhanced yellow fluorescent protein (eYFP) in dorsal and ventral dentate gyrus (DG).
(A) A virus cocktail of AAV9-c-Fos-tTA and AAV9-TRE-eYFP was infused into the dorsal or ventral DG in mice on a doxycycline diet (Dox). (B) Dox was removed prior to placement in Context A and returned to diet following exposure to label active cells with eYFP. The following day, mice were returned to the same or different context and expression of c-Fox was visualized. (C–F) Representative images (20X) of eYFP+ (green), c-Fos+ (red), and overlap of cells in the dorsal (dDG) or ventral (vDG) dentate gyrus. eYFP+, c-Fos+, and overlap in mice exposed to a different (C & E) or the same (D & F) context. (G & H) In the dorsal DG, 4.7% (+/−0.7%) of DAPI+ cells were labeled with eYFP while Off Dox compared to <0.3% of On Dox (t(18)=6.58, p<0.01). (I) Mice exposed to the same context (Context A; tagged) had significantly more overlap between eYFP+ and c-Fos+ granule cells than those exposed to a different context (Context B; untagged) relative to chance (dashed line; n=10/group) (t(18)=3.24, p<0.01). Both Contexts A and B recruited similar amounts of cFos+ and eYFP+ cells (inset). (J & K) In the ventral DG, 2.1% (+/−0.2) of ventral DG granule cells were labeled while Off Dox compared to < 0.3% while On Dox (t(18)=7.96, p<0.01) (top; n=10/group). (L) Re-exposure to the same or different context did not result in significant overlap relative to chance (ns) (bottom; n=4/group). The number of cFos+ and eYFP+ cells was comparable between both Contexts A and B (inset). White arrows indicate cells expressing eYFP and c-Fos.