Fig. 3. A) Effect of B2G2 on CD44+-α2β1high expression in human PCa C4–2B and DU145 cells.
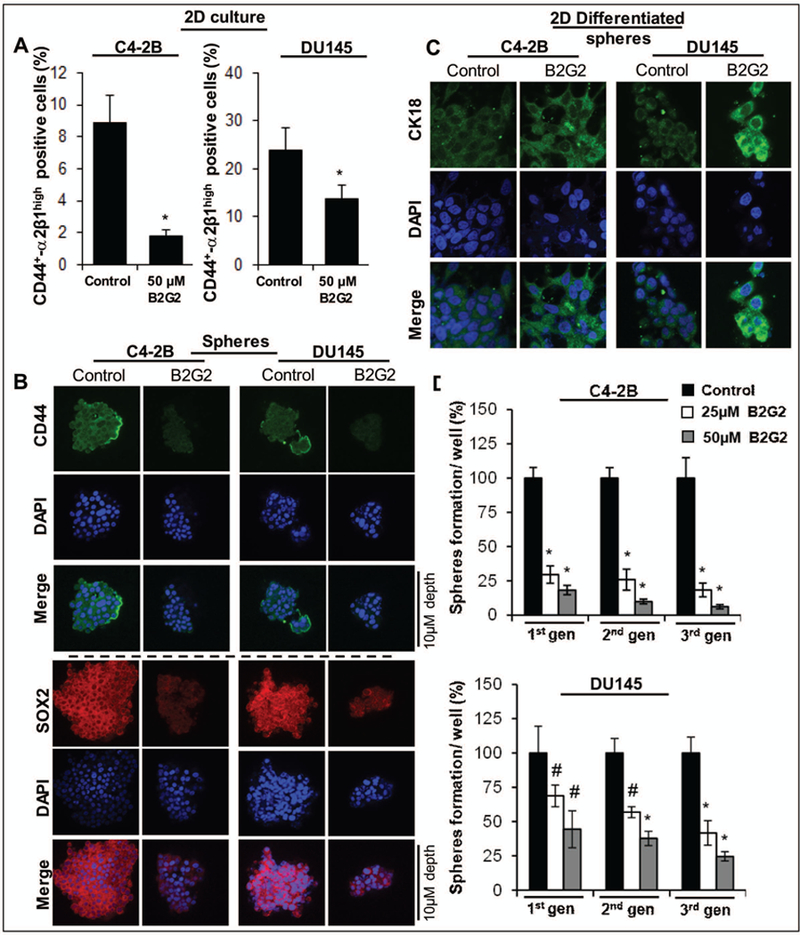
The bar graph shows the percentage of CD44+-α2β1high positive cells in B2G2 treated group vs. their respective DMSO controls. In all bar graphs, statistical differences are shown w.r.t. DMSO controls. B) Effect of B2G2 on protein expression of CSC associated-marker CD44, and -transcription factor SOX-2 in C4–2B and DU145 prostaspheres. Z stack analysis was performed as detailed in ‘Materials and Methods’ section and representative scans (X 600) with individual scan depth of specific prostaspheres are shown. C) Effect of B2G2 on 2D differentiation of CSC enriched prostaspheres. For 2D differentiation, prostaspheres (with or without B2G2 treatment) were allowed to differentiate under adherent culture conditions in the presence of regular culture media (with 10% FBS). Representative IF staining photomicrographs (X600 magnification using confocal microscopy) of 2D differentiated prostaspheres with CK18 and DAPI as nuclear stain are shownx. D) Persistent inhibitory effect of B2G2 on prostasphere formation after sub-culturing in different generations in the absence of B2G2. Equal number of viable C4–2B and DU145 PCa cells from 1st generation prostaspheres (with or without B2G2 treatment) were re-plated for 2nd generation sphere cluster assay and this was process was repeated to generate 3rd generation spheres. The bar graph shows the percentage of prostaspheres formation from cells derived from prostaspheres previously exposed to B2G2 vs. DMSO treated controls. #; P<0.01; *; P<0.001. C, control; B2G2, procyanidin B2 3, 3″-di-O-gallate.
