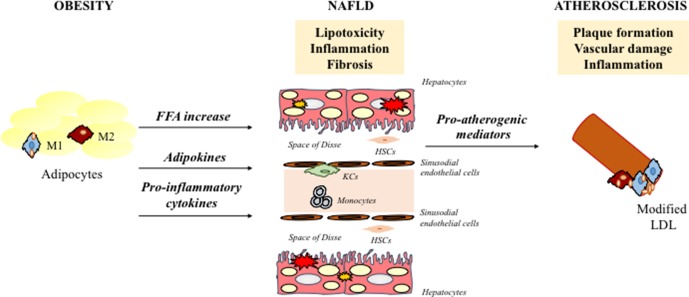
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of key mechanisms responsible for NAFLD associated-atherosclerosis. NAFLD contributes to a more atherothrombotic risk profile via atherogenic dyslipidemia, hepatic/systematic insulin resistance and increased secretion of several proinflammatory and pro-coagulant mediators. NAFLD, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; HSCs, hepatic stellate cells; FFA, free fatty acids; LDL, low-density lipoproteins; KCs, kupffer cells.