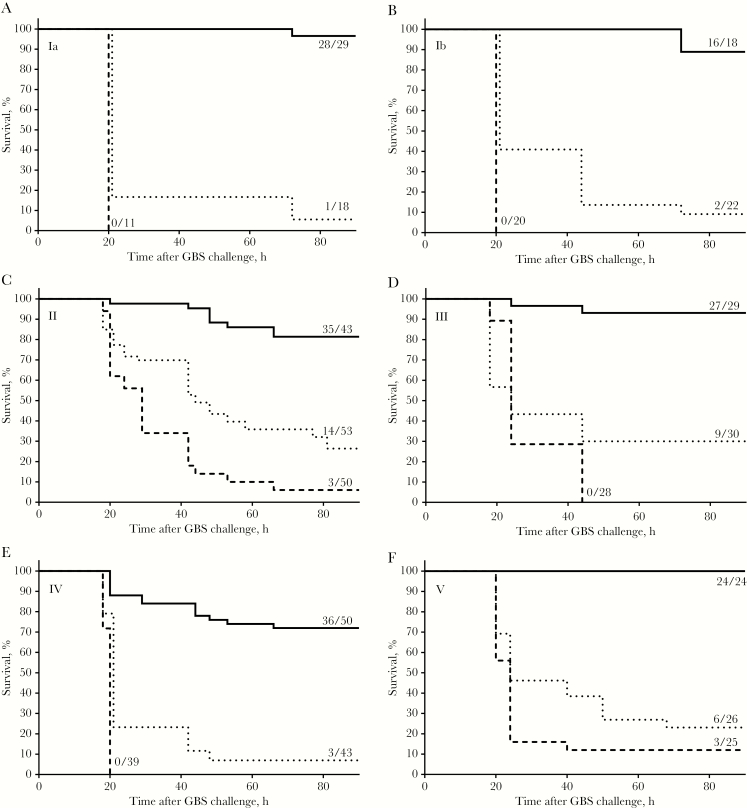
Figure 3.
Passive immunization of dams with capsular polysaccharide-specific monoclonal antibody (mAb) protects pups against a lethal dose of group B streptococcus (GBS) bacteria of the corresponding serotype. Pups born to dams immunized 24–48 hours prior to delivery with phosphate-buffer saline (dotted line), 500 μg of unrelated immunoglobulin G (IgG) control mAb (dashed line), or 500 μg of capsular polysaccharide serotype–specific IgG mAb (straight line) were challenged within 24 hours after birth (day 0) with 105–107 colony-forming units, depending on serotype. Ratios indicate the number of surviving pups 90 hours after the challenge and the total number of pups tested. Protection by capsular polysaccharide–specific antibodies versus phosphate-buffered saline was statistically significant (P < .0001) for all serotypes.