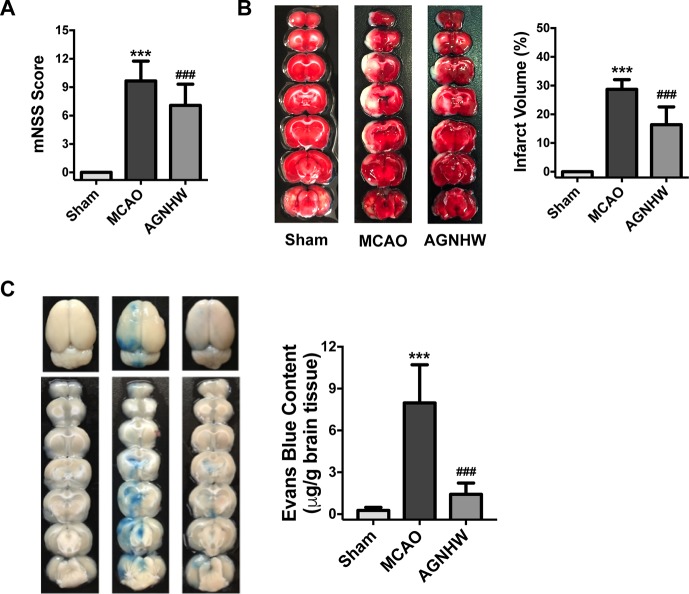
Figure 2.
AGNHW ameliorated middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO)-induced neurological deficits, decreased infarct size, and preserved blood–brain barrier (BBB) integrity. Male Sprague–Dawley (SD) rats were subjected to 2 h of ischemia and 22 h of reperfusion to establish the MCAO model. AGNHW (257 mg/kg, suspended in saline) was given to animals before reperfusion. (A) Modified Neurological Severity Score (mNSS) was evaluated 24 h after the onset of ischemia–reperfusion based on an 18-point scale (n = 12). (B) Infarct size measured by TTC staining 24 h after the onset of ischemia–reperfusion (n = 10). (C) Evans blue content measured 24 h after the onset of ischemia–reperfusion (n = 10). All data are means ± S.E.M. The significance of differences was from Sham at ***p < 0.001 and from MCAO at ### p < 0.001.