Figure 1.
Diffusion Tensor Cardiac Magnetic Resonance
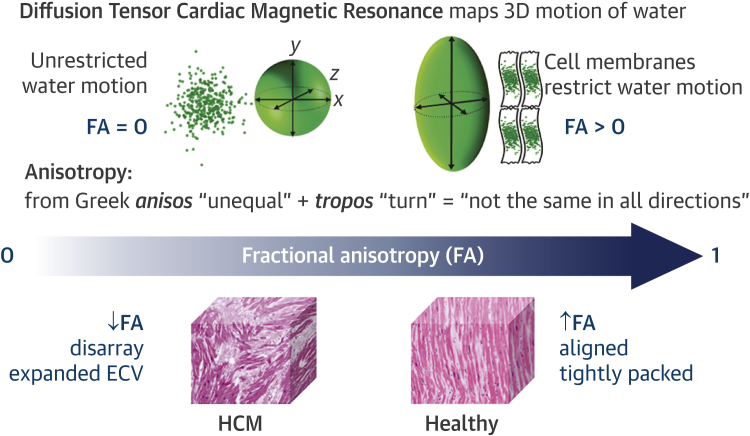
Diffusion tensor cardiac magnetic resonance (DT-CMR) maps the diffusion of water molecules in 3 dimensions (3D). Fractional anisotropy (FA) calculated from the diffusion tensor quantifies the directionality of water diffusion within each imaging voxel (2.8 × 2.8 × 8 mm3) as its motion is impeded by several million myocytes and the surrounding interstitium. Without barriers, water motion is random and equal in all directions, which can be represented as a sphere using the diffusion tensor and has an FA of zero (perfect isotropy). Cell membranes act as barriers restricting water motion along the long axis of myocytes. Thus, FA is expected to be high in voxels with coherently aligned myocytes with a consistent orientation. Conversely, FA is expected to be low in voxels with differing myocyte orientations and in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) due to disorganized cell orientations and expanded extracellular volume (ECV) (39).