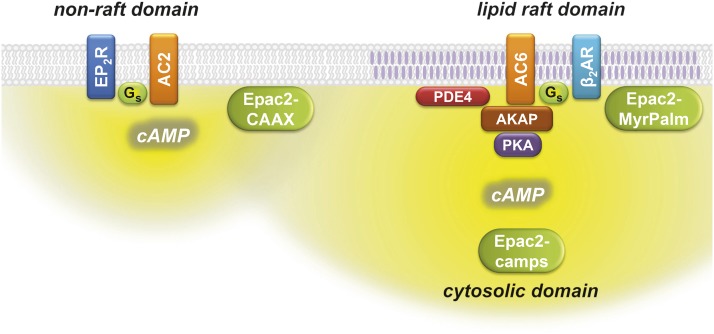
Fig. 6.
Compartmentalized cAMP signaling in human airway smooth muscle cells. β2AR stimulation of AC6 produces cAMP that is most readily detected by the Epac2-MyrPalm biosensor, which is targeted to lipid raft domains of the plasma membrane, and the Epac2-camps biosensor, which is expressed throughout the cytosolic domain. AKAPs contribute to the formation of a signaling complex that includes β2ARs, AC6, type II PKA, and PDE4 associated with lipid raft membrane domains. EP2Rs stimulation of AC type 2 (AC2) produces cAMP that is most readily detected by the Epac2-CAAX biosensor, which is targeted to nonraft membrane domains.