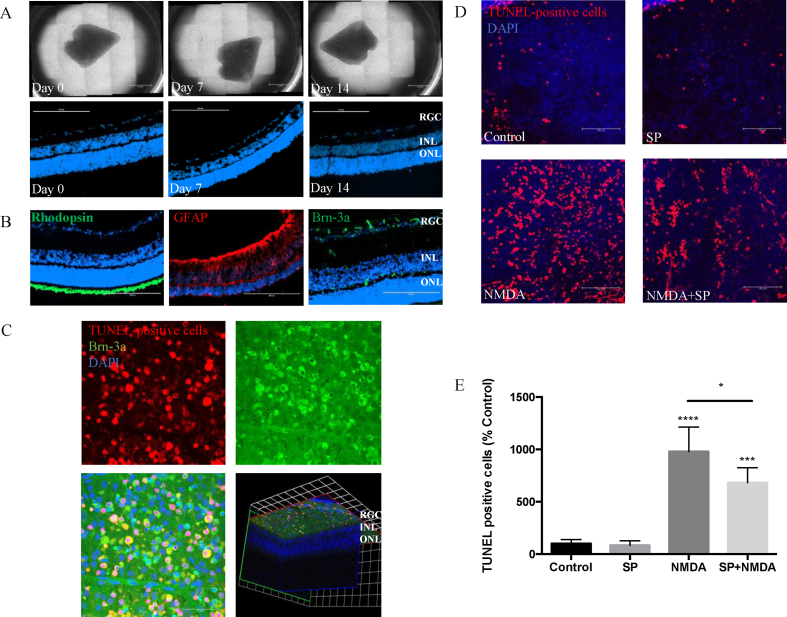
Fig. 4.
Substance P protects against apoptotic cell death in the retinal explants induced by NMDA. Gross morphology and tissue viability of rat retinal explants, cultured in B27/N2 and maintained to Day 14. (A) Wholemount photographs. Scale bar, 2 mm. Sectioned explants, stained with DAPI to visualize nuclei, demonstrated good survival of cells in the ganglion cell layer (GCL), inner nuclear layer (INL), and outer nuclear layer (ONL). Scale bar, 200 μm. (B) Immuno-staining of retinal sections from day 14 explant for different cell markers (Rhodopsin, Brn-3a, GFAP), counterstained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 200 μm. (D, E) Representative images showing TUNEL-positive cells in rat explants exposed to NMDA (10 μM), SP (20 μM) or pretreated with SP 6 h before NMDA exposure (n = 6 per group). Scale bar, 100 μm. Quantification of TUNEL positive cells expressed as percentage of control. (C) Representative images of retinal wholemount obtained from eyes exposed to NMDA for 24 h (10 nmol, intravitreal injection), showing TUNEL+ (red), Brn-3a+ (green), and cell nuclei stained with DAPI (blue). 3D image indicates NMDA specifically induced TUNEL+ in GCL. Scale bar, 50 μm. Data represents means ± SD of relative values vs control from 3 independent experiments. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001, statistical analysis was performed with one-way ANOVA with Dunn's test for multiple comparisons. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)