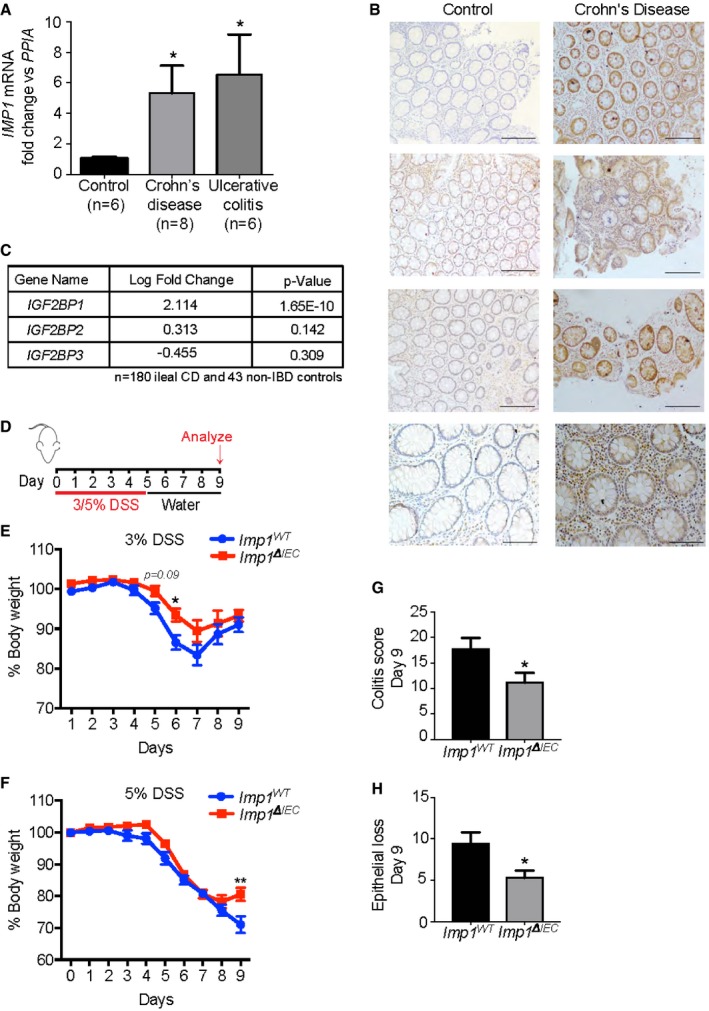
qPCR analysis for IMP1 expression in colon biopsy samples from adult ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn's disease (CD) patients. IMP1 expression is > 5‐fold higher in UC (6.554 ± 2.609, n = 6; P‐value = 0.0302) and CD samples (5.314 ± 1.807, n = 8; P‐value = 0.0343) as compared to control samples (1 ± 0.1245, n = 6).
Representative immunohistochemistry demonstrating IMP1 expression in colon biopsy samples from CD patients and normal adults (Scale bars = 500 μm).
Differential gene expression analysis of pediatric ileal CD patient samples (n = 180) shows increased (> 4‐fold) IMP1 expression as compared to non‐inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) pediatric samples (n = 43).
Experiment schematic. Mice were given either 3% or 5% dextran sodium sulfate (DSS) in drinking water for 5 days followed by 4 days of recovery.
With 3% DSS, mice with Imp1 deletion [Imp1
ΔIEC (n = 8)] lost significantly less weight compared to controls (Imp1
WT (n = 18); P‐value = 0.0259 at day 6).
With 5% DSS, Imp1
ΔIEC mice began to regain weight at day 9 compared to controls (Imp1
WT (n = 22) and Imp1
ΔIEC (n = 16; P‐value = 0.0104).
Imp1
ΔIEC mice show significantly less total colitis (11.14 ± 1.933, n = 7; scored blinded by a pathologist) as compared to Imp1
WT mice (17.75 ± 2.144, n = 8) after 5% DSS (P‐value = 0.0415).
Imp1
ΔIEC mice show significantly less epithelial loss (5.286 ± 0.865, n = 7) as compared to Imp1
WT mice (9.375 ± 1.375, n = 8) after 5% DSS (P‐value = 0.0303).
Data information: All data are expressed as mean ± SEM. *
‐test (for DSS weights, significance was determined using the Mann–Whitney test).