Figure 7. IMP1 contributes to colonic epithelial repair in part via modulation of autophagy.
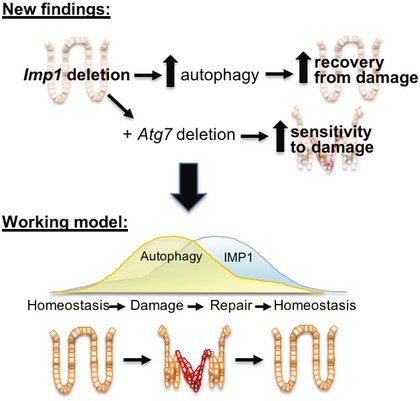
We demonstrate that Imp1 deletion enhances autophagy flux and promotes better recovery from DSS‐induced damage. Deletion of Atg7 in mice with Imp1 deletion increases sensitivity to damage, suggesting that pathways regulated by Imp1 may normally compensate for autophagy loss. These data contribute to a working model whereby dynamic regulation of Imp1 during injury may serve to modulate autophagy during the reparative response.
