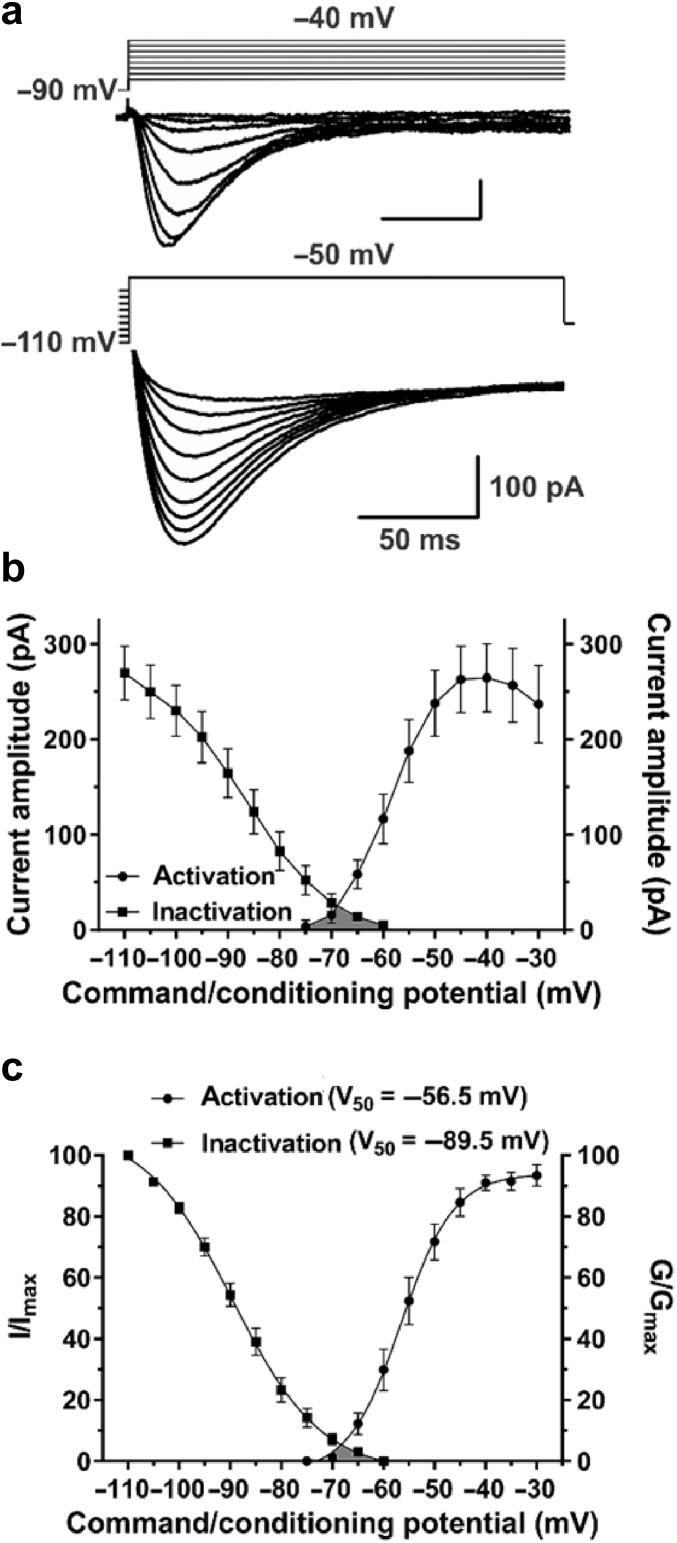
Fig 1.
Biophysical properties of T-type calcium currents (T-currents) in the juvenile rat subiculum. (a) Average T-current I-V traces from representative subicular neurones for Vt from −75 to −40 mV (the peak of activation) from Vh of −90 mV in 5 mV increments (top), and traces generated using a double-pulse protocol with 3.6-s prepulses to variable voltages (from −110 to −70 mV in 5 mV increments) and test potential of −50 mV (bottom); not all data points are displayed. (b) Average current amplitudes of the voltage dependence for activation and steady-state inactivation. (c) The voltage dependence of activation (G/Gmax) and steady-state inactivation (I/Imax) is shown with V50 values noted in the parentheses. Note the ‘window’ current depicted by the grey area below the intersection of the curves. Results are expressed as mean (standard error of mean).