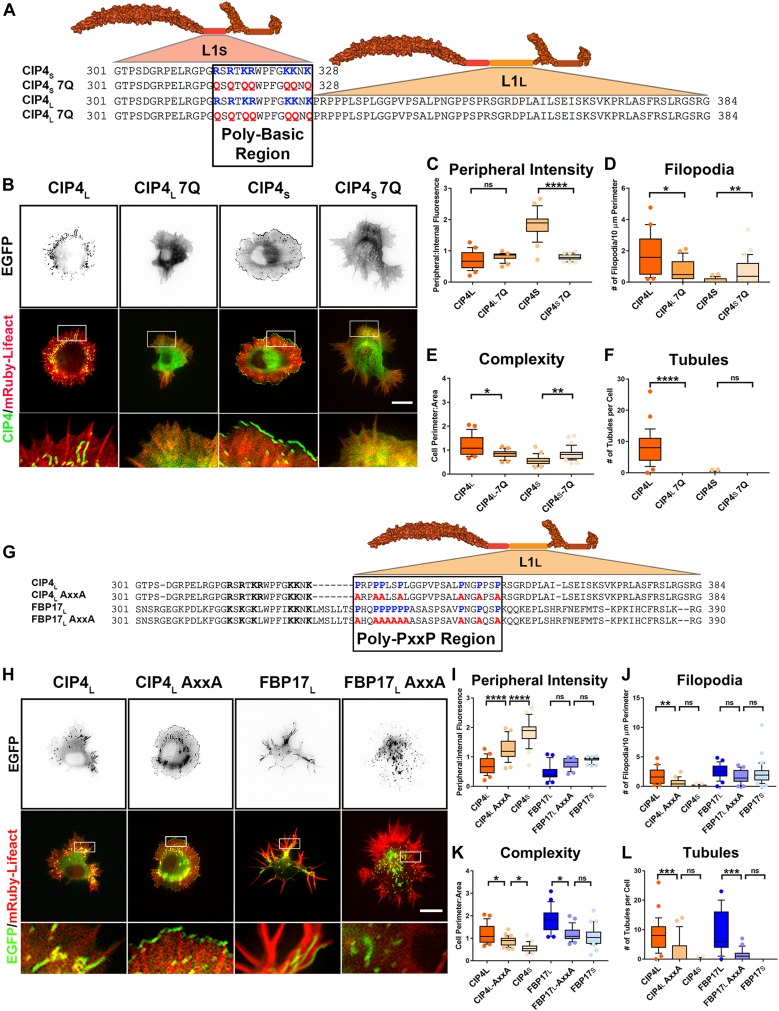
Figure 6. The PBR is required for membrane bending and the poly-PxxP region is required for tubulation in cortical neurons.
(A) Schematics of the CIP4 L1 PBR in the short and long isoforms, highlighting basic amino acids (K/R) in blue and the K/R-Q mutations in red. (B) Images of living cortical neurons cotransfected with mRuby-Lifeact and EGFP-labeled proteins or mutant proteins 12 h postplating. (C–F) Quantification of stage 1 neurons comparing the effects of the 7Q mutationson peripheral intensity (C), filopodia number (D), cell complexity (E), and tubule number (F) 12 h postplating. CIP4L-EGFP (n = 29 cells), CIP4L-7Q-EGFP (n = 28 cells), CIP4S-EGFP( = 24 cells), or CIP4S-7Q-EGFP (n = 34 cells). (G) Schematic of the L1L in CIP4L and FBP17L showing the PxxP motifs highlighted in blue and the AxxA mutations highlighted inred. (H) Images of living cortical neurons cotransfected with mRuby-Lifeact and either EGFP-labeled protein or mutant 12 h postplating. (I–L) Quantification of stage 1 neurons comparing the effects of the AxxA mutations on peripheral intensity (I), filopodia number (J), cell complexity (K), and tubule number (L) 12 h postplating. CIP4L-EGFP (n = 29 cells), CIP4L-AxxA-EGFP (n = 29 cells), CIP4S-EGFP (n = 24 cells), FBP17L-EGFP (n = 23 cells), FBP17L-AxxA-EGFP (n = 25 cells), or FBP17S-EGFP (n = 31 cells). One-way ANOVA with Kruskal–Wallis post-test multiple comparisons. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001; ns, not significant. Scale bars represent 5 µm in whole-cell images and 1 µm ininsets.