Figure 1.
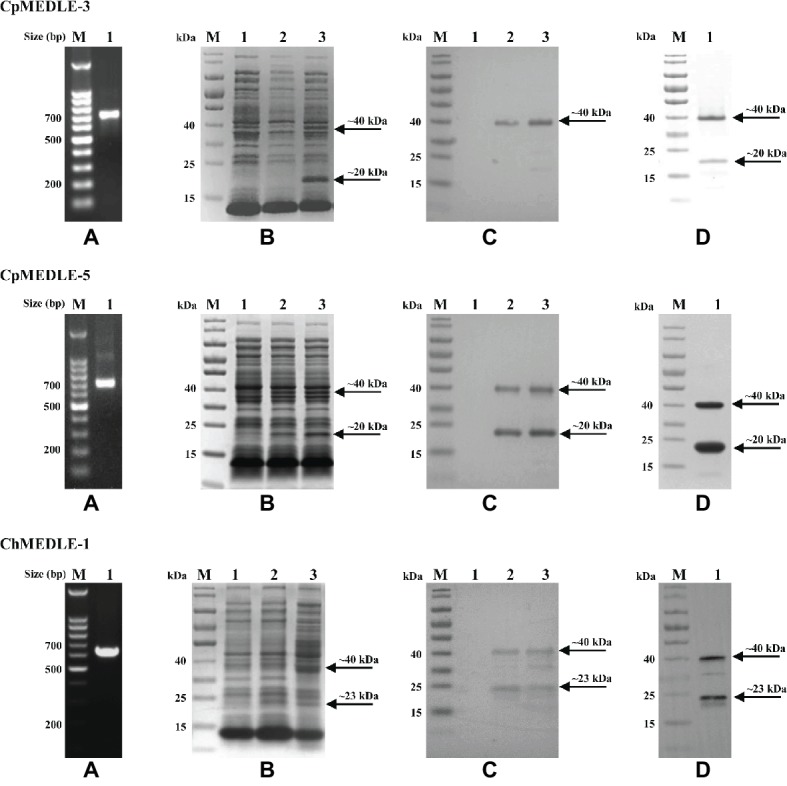
Production and purification of recombinant MEDLE proteins CpMEDLE-3 and CpMEDLE-5 from Cryptosporidium parvum and ChMEDLE-1 from Cryptosporidium hominis. (A) PCR amplification of the target gene in genomic DNA. Lane M: molecular markers; lane 1: PCR product. (B) Expression of recombinant MEDLE protein in E. coli BL21 (DE3) as revealed by SDS-PAGE analysis. Lane M: molecular weight markers; lane 1: lysate from bacteria culture transformed with the recombinant plasmid without IPTG induction; lane 2: lysate from similar bacteria culture induced by IPTG for 2 h; lane 3: lysate from bacteria culture induced by IPTG for 8 h, with the expected product indicated by an arrow. (C) Western blot analysis of the recombinant protein. Lane M: molecular weight markers; lane 1: lysate from bacteria culture transformed with recombinant plasmid without IPTG induction; lane 2: supernatant from IPTG-induced bacterial culture; lane 3: cell lysate from IPTG-induced bacterial culture. (D) Purification of recombinant proteins. Lane M: molecular weight markers; lane 1: purified recombinant proteins from Ni-NTA affinity chromatography.
