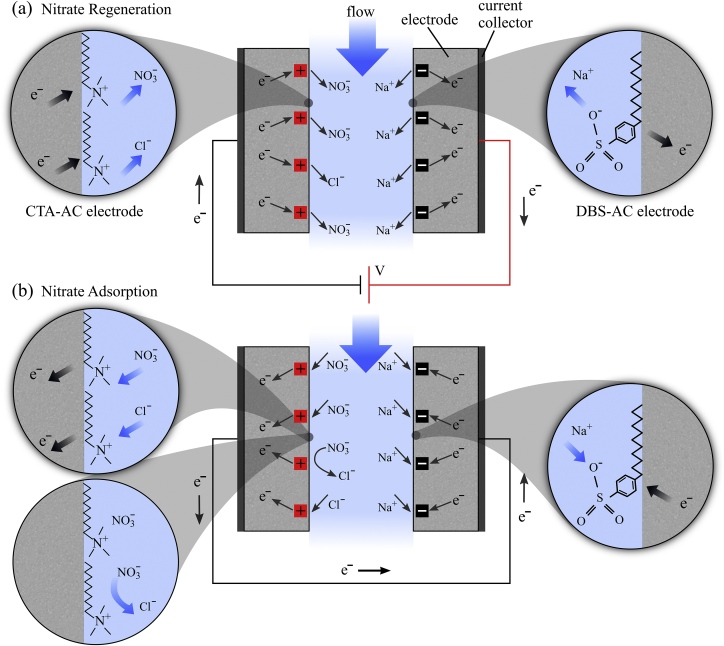
Fig. 1.
Schematic of the i-CDI cell used in this study. One electrode (labeled CTA-AC) is treated with CTAB and a counter electrode (DBS-AC) is treated with SDBS. (a) Schematic of the regeneration step at constant voltage of the i-CDI cell. The applied bias forces electrons to migrate from DBS-AC to CTA-AC. Electrons driven toward CTA-AC repel Cl- and NO3- ions, while holes driven toward DBS-AC repel Na + ions. This process leaves an available surface charge in both electrodes (DBS-AC to CTA-AC). (b) Schematic of a simple short-circuit adsorption process. , , and ions are adsorbed, forcing migration of electrons from CTA-AC to DBS-AC.