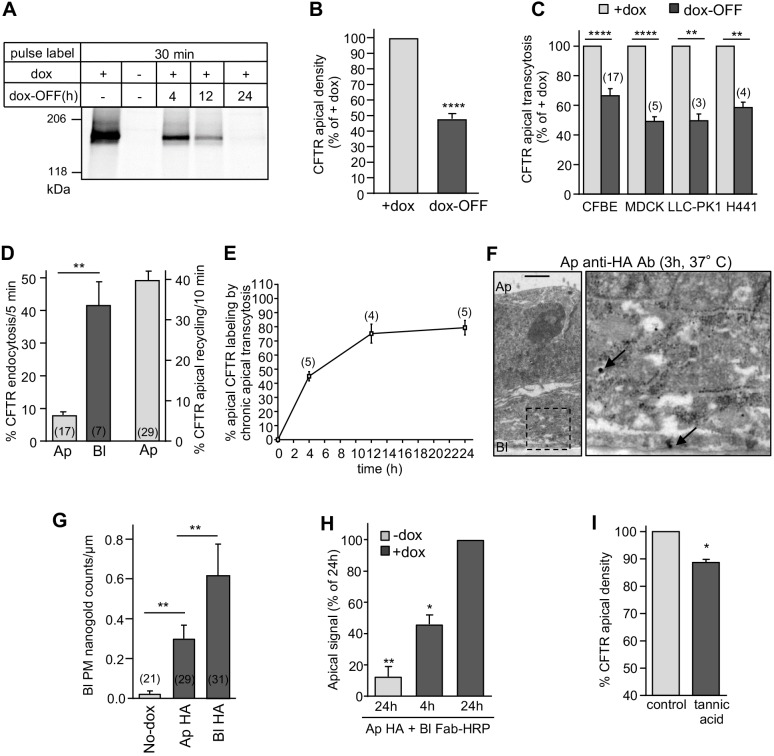
Fig. 3.
Apical transcytosis retrieves basolaterally missorted CFTR from the biosynthetic and apical recycling pathways. (A) Onset of CFTR translational arrest in dox-OFF CFBE. Translational inhibition was measured by metabolic pulse labeling with 35S-metionine/35S-cysteine (30 min) after 0–24 h of dox-OFF (i.e. after washout) by fluorography. (B,C) CFTR apical density in CFBE cells (n=12) (B) and apical transcytosis after 24 h of dox-OFF in the indicated epithelial cells (C). (D) CFTR endocytosis and recycling in CFBE cells monitored by PM-ELISA (two-tailed unpaired t-test). (E) Apical CFTR labeling after basolateral-to-apical transcytosis. CFTR was labeled by continuous basolateral anti-HA capture at 37°C. Apical CFTR-Anti-HA Ab complexes were measured by PM-ELISA. (F,G) CFTR basolateral transcytosis detection by immuno-EM in CFBE cells after apical capture of anti-HA Ab (3 h, 37°C). The micrograph on the right is a higher magnification of the selected area. Arrows, CFTR-anti-HA-nanogold-anti-mouse complex. Scale bar: 1 µm. (G) Quantification of the number of nanogold particles at the basolateral PM after apical or basolateral anti-HA Ab uptake (data extracted from Fig. 2C, n=2–3 independent experiments, Mann–Withney U-test). (H) ‘Round-trip’ CFTR transcytosis was monitored by simultaneous exposure of CFBE to anti-HA and anti-mouse Fab–HRP in the apical and basolateral compartment, respectively, for 4 h or 24 h. Transcytosed CFTR was quantified by PM-ELISA (n=3). (I) Inhibition of transcytosis accelerates apical CFTR turnover. After blocking newly synthesized CFTR arrival (dox-OFF, 24 h), CFBE cells were exposed basolaterally to 0.5% tannic acid (15 min, 37°C) or mock treatment. Apical CFTR density was measured after 1 h incubation at 37°C by PM-ELISA (n=3) and expressed as a percentage of control. Ap, apical; Bl, basolateral. Data are means±s.e.m. on each panel, parentheses indicate the number of independent experiments (C–E) or regions of interest (G). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ****P<0.0001.