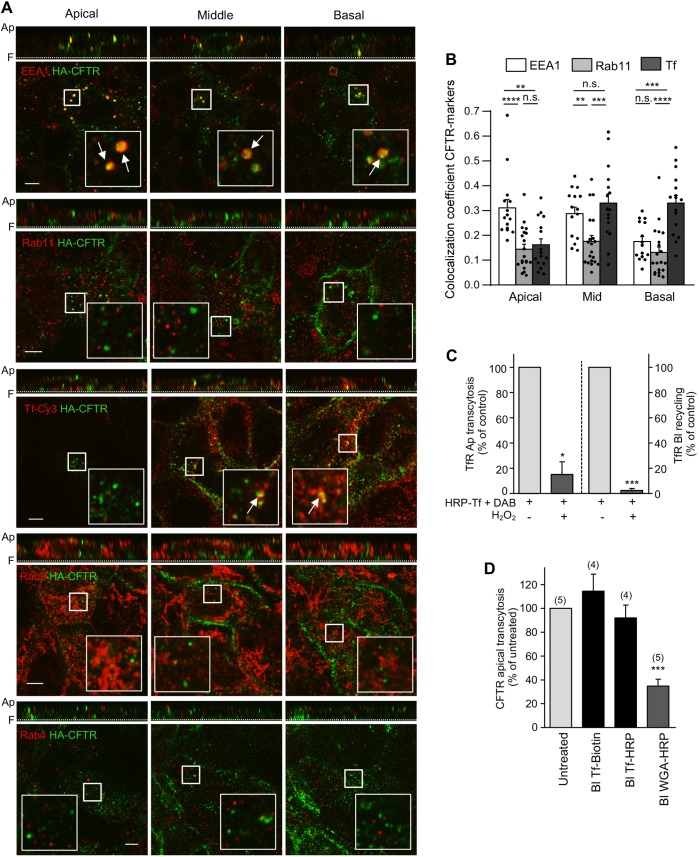
Fig. 4.
Apical transcytotic route of CFTR in polarized CFBE. (A) Immunocolocalization of transcytotic CFTR. CFTR was labeled by basolateral anti-HA Ab capture (45 min, 37°C), while staining of apically delivered CFTR-anti-HA complexes were blocked with goat anti-mouse Fab. Then, the colocalization of transcytotic CFTR–anti-HA (green) with EEA1, Rab11, Rab4 or Rab8 (red) was determined by indirect immunostaining and laser confocal fluorescence microscopy at the apical, middle, and basal planes of filter-grown CFBE cells (lower panels). Vertical optical sections are shown as top panels. TfR was labeled by means of Cy3–Tf uptake (45 min). Inserts represent a ∼3.5-fold magnification of the selected area. Ap, apical PM; F, filter. Arrows indicate colocalization. (B) Quantitative colocalization of transcytosed CFTR with organellar markers. The Manders' colocalization coefficient was calculated on each slice of 3D-volumes [n=15 (EEA1), 20 (Rab11) and 16 (Tf) z-stacks from three independent experiments] that were divided into three approximately equal sections (apical, middle and basal). Two-tailed unpaired t-test. (C) Functional inactivation of TfR-containing endosomes. Tf–HRP was basolaterally loaded (30 min, 37°C) and incubated with H2O2 and DAB or DAB alone (control). Apical (Ap) transcytosis or basolateral (Bl) recycling of Tf–HRP was measured as described in the Materials and Methods and expressed as percentage of control (n=3). (D) CFTR apical transcytosis is largely independent of the TfR trafficking route but intersects with BSEs. Following functional ablation of Tf–HRP- or HRP–WGA-loaded endosomes, CFTR apical transcytosis was measured for 3 h at 37°C. Tf–biotin was used as control. Parentheses indicate the number of independent experiments. Data are means±s.e.m. on each panel. *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001; ****P<0.0001; n.s., not significant.