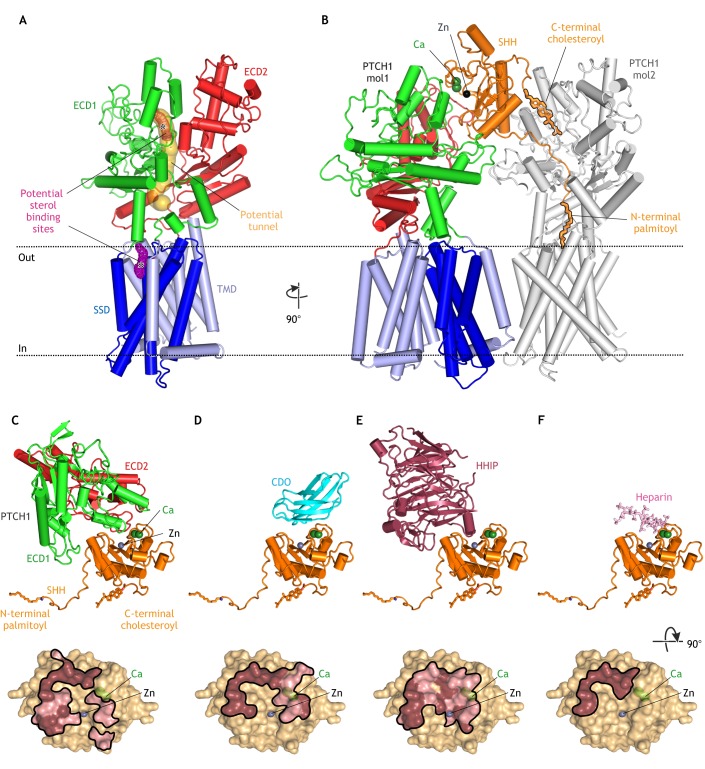
Fig. 2.
Structures of PTCH. (A) Structure of unliganded PTCH (PDB 6DMB; Gong et al., 2018) showing the transmembrane domain (TMD), which includes a sterol-sensing domain (SSD), and two extracellular domains (ECD1 and ECD2). A possible hydrophobic tunnel (ocher surface) is shown connecting two putative sterol-binding sites (meshed surfaces, asterisks) in ECD1 and the SSD. (B) Structure of the asymmetric 1SHH:2PTCH complex (adapted from PDB 6E1H; Qi et al., 2018b) reveals two distinct SHH-PTCH interfaces. PTCH1 molecule 1 (mol1) binds to SHH at an interface including its calcium- and zinc-binding sites and PTCH1 molecule 2 (mol2) engages the N-terminal palmitoyl and C-terminal cholesteroyl modifications of SHH, which are inserted into the PTCH protein core. The interaction of SHH with mol1 drives PTCH endocytosis and the palmitate-centered interaction with mol2 inactivates the transporter function of PTCH. (C-F) Structures of SHH in complex with the PTCH ECD (C; adapted from PBD 6E1H), CDO (D; PDB 3D1M; McLellan et al., 2008), HHIP (E; PDB 2WFX; Bishop et al., 2009) and heparin (F; PDB 4C4N; Whalen et al., 2013) reveal overlapping interfaces that would prevent simultaneous binding. Binding footprints for each protein on SHH are shown below the corresponding structure, with hydrophilic interactions in pink and hydrophobic interactions in brown.