Fig. 5.
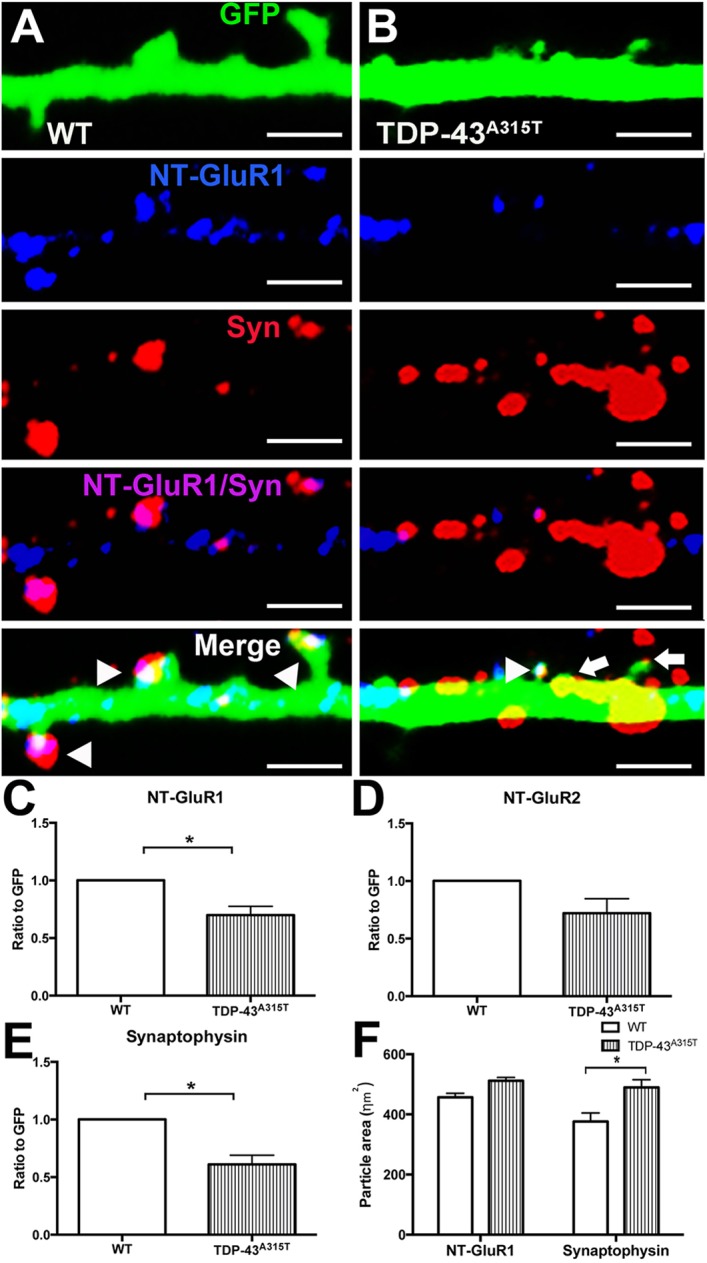
The effect of TDP-43A315T expression at the synapse. (A) Immunocytochemistry for NT-GluR1 (blue), synaptophysin (Syn, red) and GFP (green) demonstrated that NT-GluR1 and synaptophysin colocalized at the dendritic spine (white) in YFP:WT dendrites (A, arrowheads). (B) In YFP:TDP-43A315T dendrites, immunocytochemistry for NT-GluR1 (blue), synaptophysin (red) and GFP (green) demonstrated that spines were present that colocalized for NT-GluR1 and synaptophysin (white; arrowhead), with spines also present lacking NT-GluR1 (arrows); frequent accumulations of synaptophysin were observed outside the identified dendritic spines. (C) Quantification of the ratio of NT-GluR1 to GFP demonstrated significant decrease in the colocalization of NT-GluR1 in TDP-43A315T cortical neurons in comparison to WT controls. (D) Quantification of the ratio of NT-GluR2 to GFP demonstrated no significant change in the ratio of colocalization of NT-GluR2 in TDP-43A315T cortical neurons in comparison to WT controls. (E) Quantification of the ratio of synaptophysin to GFP showed significant decrease in the colocalization of synaptophysin in TDP-43A315T cortical neurons in comparison to WT controls. (F) Quantification of the particle size of NT-GluR1 and synaptophysin demonstrated that there was a significant increase in the area of the synaptophysin particles in TDP-43A315T cortical neurons in comparison to WT controls. n=3 biological replicates. *P<0.05 (Student's t-test and two-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons test). Data are mean±s.e.m. Scale bars: 1 μm.
