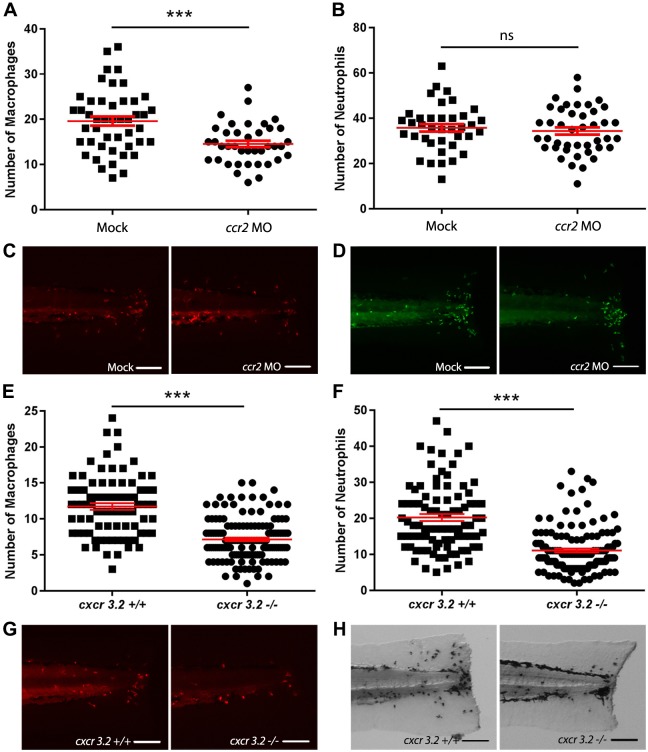
Fig. 4.
Effect of ccr2 morpholino knockdown or cxcr3.2 mutation on macrophage and neutrophil recruitment upon tail amputation in larvae. (A-B) The number of macrophages (A) and neutrophils (B) recruited to the wounded area at 4 hpa in 3dpf Tg(mpx:GFP/mpeg1:mCherry-F) larvae. In ccr2 morpholino-injected larvae, a significantly reduced number of macrophages were recruited compared to the number in mock (vehicle)-injected larvae. No significant difference was observed for the number of recruited neutrophils. (C-D) Representative images of the macrophages (fluorescently labeled by mCherry) (C) and the neutrophils (fluorescently labeled by GFP) (D) of mock-injected and ccr2 morpholino-injected larvae at 4 hpa. (E-F) The number of macrophages (E) and neutrophils (F) that recruited to the wounded area at 4 hpa in 3 dpf Tg(mpeg1:mCherry-F) larvae. A significantly reduced number of macrophages and neutrophils were recruited in cxcr3.2 mutant larvae compared to the number in wt controls. (G-H) Representative images of the macrophages (fluorescently labeled by mCherry) (G) and the neutrophils (stained using MPX assay) (H) of wt and cxcr3.2 mutant larvae at 4 hpa. Data are mean±s.e.m. (indicated in red), pooled from three independent experiments. ***P<0.001 (determined using the two-tailed t-test). ns, non-significant. Scale bars: 100 μm.