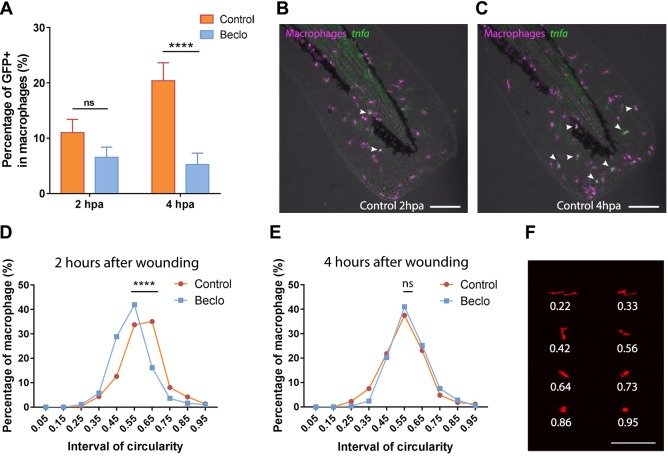
Fig. 8.
Effect of beclomethasone on the phenotype of macrophages. (A) In Tg(mpeg1:mCherry-F/tnfa:eGFP-F) reporter larvae, the number of GFP-positive macrophages (as a percentage of the total number of macrophages) recruited to the wounded area was quantified at 2 and 4 hpa in 5 dpf larvae. In the beclomethasone-treated group (Beclo), at 4 hpa, a significantly reduced percentage of the recruited macrophages was GFP-positive compared to the vehicle-treated group (Control). Data are mean±s.e.m. ****P<0.0001 (determined using ANOVA with a Fisher's LSD post hoc). (B-C) Representative images of macrophages (fluorescently labeled by mCherry) and GFP-positive macrophages (fluorescently labeled by both mCherry and GFP) in the control group at 2 hpa (B) and 4 hpa (C). Arrowheads indicate macrophages displaying the GFP signal, which is a measure for activation of the tnfa promoter. (D-E) The distribution of circularity of macrophages recruited to the wounded area at 2 h after wounding (hpa) (D) and at 4 h after wounding (E) in 3 dpf Tg(mpeg1:mCherry-F) larvae. At 2 hpa, a significant difference of distribution pattern was observed between the two groups, with the beclomethasone-treated group (Beclo) shifted towards lower circularity. At 4 hpa, no significant difference was observed. ****P<0.0001 (determined using the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test). (F) Representative images of macrophages analyzed in D and E and their corresponding circularity. ns, non-significant. Scale bars: 100 μm.