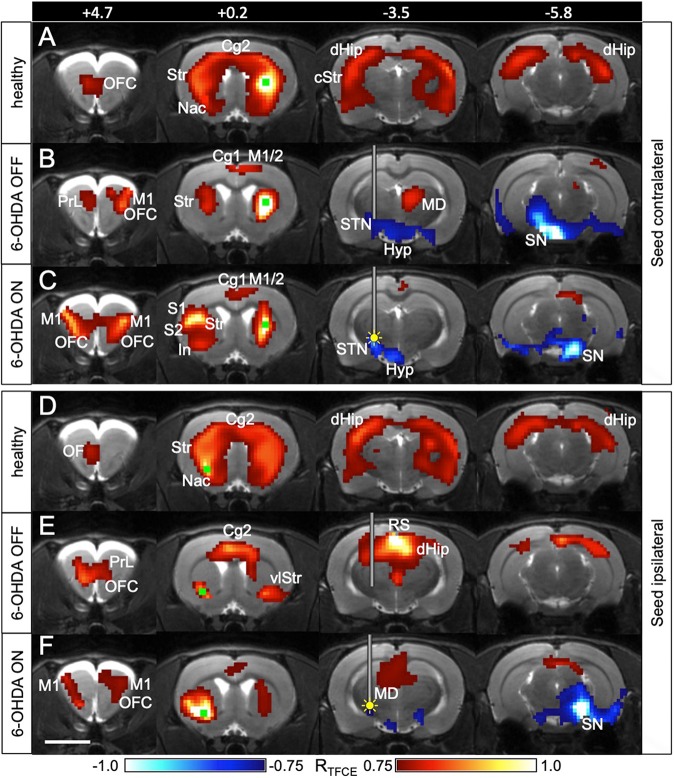
Fig. 3.
Striatal connectivity is changed by STN-DBS. (A-C) Connections of the healthy striatum are changed by STN-DBS. The seed (green square) was placed contralateral to the 6-OHDA injection in 6-OHDA animals (n=7) and in the right striatum in healthy controls (n=19). A Pearson correlation analysis was performed between the seed region and all other voxels of the brain. Yellow filled circle indicates inserted electrode and ongoing stimulation (DBS ON). (D-F) Connections of the dopamine-depleted striatum are changed by STN-DBS. The seed (green square) was placed ipsilateral to the 6-OHDA injection in 6-OHDA animals and in the left ventrolateral striatum in healthy controls. It was located exactly at the spot where STN-DBS increased [18F]FDG uptake. Red voxels, positively correlated with seed region with respect to [18F]FDG uptake. Blue voxels, negatively correlated with seed region. Numbers represent rostrocaudal coordinates (mm) relative to Bregma. The implanted guide cannula is shown in B,C,E,F. In A and D, no cannula was implanted. Cg1, cingulate cortex 1; Cg2, cingulate cortex 2; cStr, caudal striatum; dHip, dorsal hippocampus; Hyp, hypothalamus; In, insula; M1, primary motor cortex; M2, secondary motor cortex; MD, mediodorsal thalamus; Nac, nucleus accumbens; OF, orbitofrontal cortex; PrL, prelimbic cortex; RS, retrosplenial cortex; S1, primary sensory cortex; S2, secondary sensory cortex; SN, substantia nigra; STN, subthalamic nucleus; Str, striatum; vlStr, ventrolateral striatum. Scale bar: 5 mm.